Open a command prompt as follows:
Windows Vista:
Click Windows Start.
In the Search box, type Command Prompt and press ENTER.
In the result list, double-click Command Prompt.
All other Windows operating systems:
Click Windows Start > Run.
In the Run dialog box:
Windows XP, 2000, and NT: Type cmd and click OK.
Windows Me, 98, and 95: Type command and click OK.
Type Ping 127.0.0.1. This is your local host address and this will ensure that the TCP/IP protocol is installed and functioning properly. If you cannot complete this ping, refer to your Windows operating system documentation for instructions on installing TCP/IP.
Obtain IP information for your computer as follows:
Windows Vista, XP, 2000, and NT users: Type ipconfig /all and press ENTER.
Windows Me, 98, and 95 users: Type winipcfg and press ENTER.
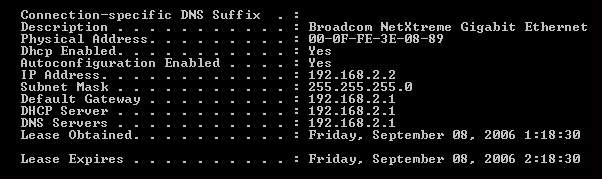
This displays IP configuration similar to the following:
Type Ping followed by the IP address displayed in step 3 and press ENTER.
This verifies whether your computer is responding to requests. If your computer's IP address is 169.254.xxx.xxx or if you cannot complete this ping, make sure all the cables are properly connected, unplug the , plug it back in, and reboot your computer.
Type Ping followed by the IP address of the access point and press ENTER.
If you can establish communication with the , you can access the configuration pages. If you cannot establish communication with the access point, make sure all the cables are properly connected, unplug it, plug it back in, and reboot your computer. If you still cannot complete this ping, refer to My wireless device is not communicating with the and skip the solutions dealing with wireless connections.
Type Ping followed by the LAN IP address, which is the Default Gateway address displayed in step 3, and press ENTER.
This verifies whether you can get past the access point to your gateway. An example of a gateway is a router.
Type Ping followed by the WAN IP address of your gateway.
This is the address that is provided either by your ISP or by the outside LAN. \ This procedure will ensure that you have access to the Internet.
Type Ping followed by the DNS server address displayed in step 3 and press ENTER.
This lets you resolve valid Internet host names to IP addresses and to verify that you can browse the Internet.
If you can successfully ping the DNS server but still cannot reach the Internet, assign your DNS servers statically as follows:
Windows Vista:
Access the configuration program or configuration pages of the networking device connected to the access point, and find the WAN status information. From that information you need the IP addresses of the WAN DNS servers. For detailed instructions, consult the documentation for the networking device.
Click Windows Start > Control Panel.
Double-click Network and Internet > Network and Sharing Center > Manage network connections.
-
Right-click the Local Area Connection of the network adapter that connects the computer to the networking device, and select Properties.
Under This connection uses the following items, select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and click Properties.
Select Use the following IP address, enter the IP addresses that you noted in step A, and click OK.
Click OK again.
Windows XP, 2000, or NT:
Access the configuration program or configuration pages of the networking device connected to the access point, and find the WAN status information. From that information you need the IP addresses of the WAN DNS servers. For detailed instructions, consult the documentation for the networking device.
Click Windows Start > Control Panel, and double-click Network Connections.
In the Network Connections window, right-click the Local Area Connection of the network adapter that connects the computer to the networking device, select Properties.
Under This connection uses the following items, select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and click Properties.
Select Use the following DNS server addresses, enter the IP addresses that you noted in step A, and click OK.
Click OK again.
Windows Me, 98, or 95:
Access the configuration program or configuration pages of the networking device connected to the access point, and find the WAN status information. From that information you need the IP addresses of the WAN DNS servers. For detailed instructions, consult the documentation for the networking device..
On the desktop, right-click Network Places or Network Neighborhood and select Properties.
On the Configuration tab, select the network adapter that connects the computer to the router and click Properties.
On the DNS Configuration tab, click Enable and enter a Host name.
In DNS Server Search Order, enter the IP address of the primary DNS server and click Add.
In DNS Server Search Order, enter the IP address of the secondary DNS server and click Add.
Click OK.
Click OK again.