
In the Web User Interface, click the Wireless tab. In this section you can configure and change the wireless network settings of the Wireless MAXg Access Point.

Note: Each wireless client in the wireless network must have Infrastructure mode selected in their Configuration Utility, as well as the correct network name (SSID) and security information, in order to connect to the Wireless MAXg Access Point. Refer to your wireless client documentation to determine how to configure these settings.
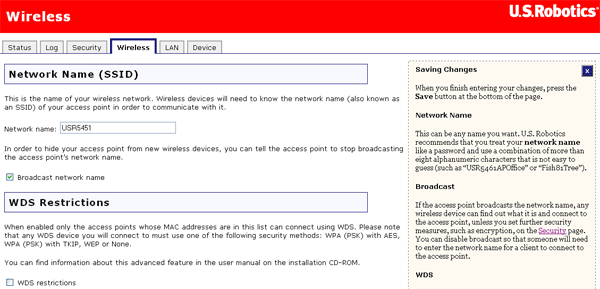
By default, the Wireless MAXg Access Point's wireless Network name is USR5451. This is used by wireless clients to identify the Wireless MAXg Access Point. We recommend you change the Network name to something unique so that you can easily identify the wireless network you want to connect to, if multiple networks are available. The Network name can be up to 26 alphanumeric characters, including underscores (_).
You can also set whether the Network name will be broadcast or by selecting or deselecting the checkbox next to Broadcast network name. If you have this enabled, the Network name will be broadcast so that anyone who is in the area and scanning for wireless devices will see your access point. If you have this disabled, only wireless clients who know your Network name will be able to locate the access point. U.S. Robotics recommends that you do not broadcast your Network name. This will increase the security of your access point.
U.S. Robotics Wireless MAXg Routers and Access Points include a a feature known as Wireless Distribution System (WDS). WDS allows networks to join wirelessly by creating a bridge between wireless routers or access points. Wireless clients are allowed to connect to the access points and routers, at the same time. Your Wireless MAXg Access Point and the wireless access point or router that you will be using to create a bridge must use the same channel and the same network name. Also, the MAC address of each bridging access point or router must be included in the WDS Restrictions table of the other bridging devices. Bridging access is limited to the MAC addresses listed a device's WDS restriction table. By default, this feature is disabled.
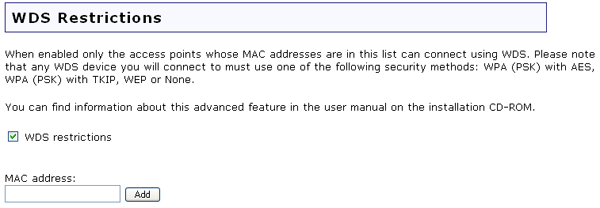
If you enable WDS, you will only be able to use the following forms of encryption methods: WPA (PSK), WEP open, WEP shared, or None. If you select WPA (PSK), you can choose either TKIP or AES, but not TKIP and AES.
Example of WDS Restrictions
One thing to note about this type of wireless network is that the throughput may be reduced for the bridging portion. Therefore, bridged routers or access points that also allow wireless clients to connect to the network should not be used for high-volume traffic. Some examples of the type of situations where you might want this type of network would be for security cameras, to provide network access to certain parts of a building that might not be able to be connected using wires, or to provide short-term network access to a conference area.
This feature is disabled by default. If you want to enable this feature, select the checkbox next to WMM. The other devices that you are connecting to in order to use this feature must also support WMM and have it enabled.
This feature enables the Quality of Service (QoS) function that is used for multimedia applications, such as Voice-over-IP (VoIP) and video. This allows the network packets of the multimedia application to have priority over regular data network packets, allowing multimedia applications to run smoother and with fewer errors.
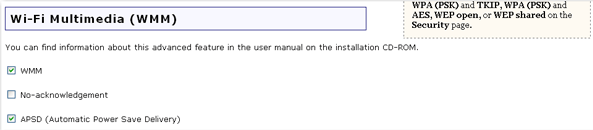
If you enable WMM, you can then select No-acknowledgement. No-Acknowledgement refers to the acknowledge policy used at the MAC level. Enabling no-acknowledgement can result in more efficient throughput but higher error rates in a noisy Radio Frequency (RF) environment.
With WMM enabled, you can also select APSD (Automatic Power Save Delivery). APSD manages radio usage for battery-powered devices to allow longer battery life in certain conditions. APSD allows a longer beacon interval until an application requiring a short packet exchange interval starts. Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) is an example of an application requiring a short packet exchange interval. APSD affects radio usage and battery life only if the wireless client also supports APSD.
Note: WMM cannot be used if Acceleration is set to MAXg (125 Mbps). You will need to change the Acceleration to either 54G+ (XPress) or None.
The fields in this area are for more advanced wireless features that most people do not need to change. If you do want to change any of these settings, write down the default settings before you make any changes in case you experience any problems and need to change these settings back.
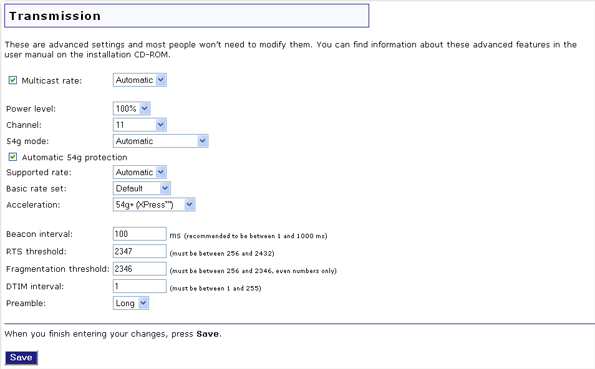
Multicast rate specifies the rate at which multicast packets are transmitted by the access point on your wireless network. Multicast packets are used to send a single message to a set of recipients in a defined group. Teleconferencing, videoconferencing and group email are examples of multicast applications. Specifying a high multicast rate may improve performance of multicast features.
You can deselect Multicast rate to prevent the access point from transmitting multicast packets.
For Power level, you can select either 100%, 50%, or 25% from the drop-down menu. The Power level sets the strength of the wireless signal that the Wireless MAXg Access Point transmits. You would want a lower setting if you live in an area where your wireless signal could be overlapping with other wireless networks and want to reduce the interference you encounter.
For Channel, you can select a different channel for your wireless network traffic to be transmitted on. If you are experiencing interference or wireless network problems, changing the channel might solve the issue.
For 54g mode, you can select Automatic, 802.11g Performance, or 802.11b Only. If you are using all 802.11g equipment, 802.11g Performance will provide the fastest performance. If you select 802.11b Only, all clients that are capable of 802.11b will connect to the Wireless MAXg Access Point at 802.11b data rates.
You can select or deselect Automatic 54g protection. If you select this option, the Wireless MAXg Access Point will use RTS/CTS to improve the 802.11g performance in 802.11 mixed environments. If this is not selected, the 802.11g performance will be maximised under most conditions while the other 802.11 modes (802.11b, etc.) will be secondary.
Supported rate is the wireless link rate at which information will be transmitted and received on your wireless network. You can select Auto, 1, 2, 5.5, 6, 9, 11, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, 54.
For Basic rate set, you can select either Default, All, or 1 & 2 Mbps.
For Acceleration, you can select None, 54g+ (Xpress™), or MAXg (125 Mbps). These features determine either normal speed rates or accelerated rates. The Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM) feature is not available if you select MAXg (125 Mbps).
Note: MAXg acceleration (125 Mbps) can be achieved only if all wireless clients connected to the access point support MAXg and your wireless environment is not noisy (no radio interference from other radio devices).
Beacon interval is the amount of time between beacon transmissions. A beacon is basically a heartbeat for a wireless client or router, sending out a signal informing the network that it is still active. This should be set between 1 and 1000 milliseconds.
RTS threshold is how long the access point will wait before sending a client an RTS message. RTS stands for Request to Send. An RTS message will tell the target computer, network, or server that the client is trying to send data and wants primary access to the computer or network during the transmission and reception of the information. If a client is experiencing difficulties transmitting data to a computer, network, or server, this threshold should be lowered.
Fragmentation threshold is the maximum level the access point will reach when sending information in packets before the packets are broken up in fragments. Typically, if you are experiencing problems sending information, it is because there is other traffic on the network and the data being transmitted is colliding. This might be corrected by the information being broken into fragments. The lower the level that the Fragmentation threshold is set to, the smaller a packet has to be before it is broken into fragments. If the maximum is set (2346), fragmentation is essentially disabled. You should only change this level if you are an advanced user.
DTIM Interval is the time between when DTIMs are sent to clients on the network. DTIM stands for Delivery Traffic Indication Message (DTIM). A DTIM is a message that is sent to clients on the network that are power-managed, informing them that there is information that needs to be sent to them so they can become active again to receive it. A smaller number means the clients will not be able to go into power saving mode for too long. A higher number means they will be able to go into power saving mode, but will have to remain active longer since more information will have accumulated to be sent to them. The default value for the DTIM interval is 1.
Preamble defines the length of the CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check) block for communication between the Wireless MAXg access point and wireless clients. Networks with a lot of traffic should select Short for the preamble, while networks without a lot of traffic should select Long for the preamble. Short preamble will boost the overall throughput of information on the wireless network. If you have Short selected and any client on the network doesn't support Short, that client will not be able to communicate with the Wireless MAXg Access Point.
After making any changes to the wireless settings of the Wireless MAXg Access Point, you must click Save in order for your changes to be saved and implemented.