The Wide Area Network (WAN) connection is your connection to the Internet or to your business network. When you are in the router interface, click the Internet tab. At the top of this page, there is a button that says Detect Connection. Click this button if you have switched your Internet connection service from DSL to cable (or vice versa) and want to have the Wireless MAXg Router attempt to automatically detect and configure your WAN connection.

When you first access this page, the Wireless MAXg Router will attempt to automatically detect and configure your WAN connection. If this is successful, you will not need to configure any settings and should be able to access the Internet. If this is not successful, you will need to manually configure your settings.
Contact your Internet Service Provider (ISP) if you need any of the following Internet connection information:
| IP Address | |
| Subnet Mask | |
| Gateway/Router | |
| DNS Servers/Name Servers | |
| User Name | |
| Password | |
| Service Name (optional) |
Select your WAN connection type from the following two choices and then enter the appropriate additional information in the order it is presented on your screen:
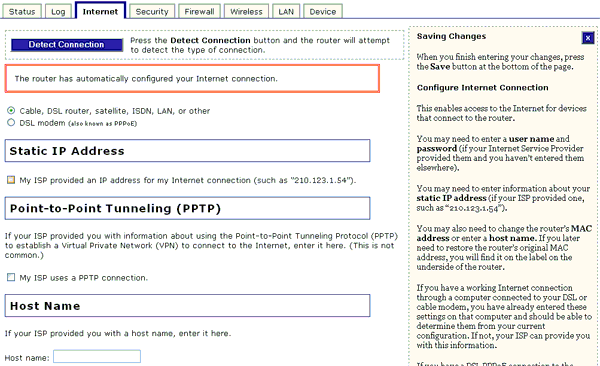
If your ISP (Internet Service Provider) gave you a static (or never-changing) IP address for your Internet connection, select this checkbox and then enter the appropriate information in the available fields for Static IP address, Subnet Mask, Gateway, DNS servers, and WINS servers. Depending on the information that was supplied by your ISP, you may not need to fill in all of these fields. If you have any questions regarding the proper setting values, contact your ISP.
If your ISP gave you a Host name for your Internet connection, enter it here. The Host Name is not the same as your User Name. If you have any questions about a Host Name, contact your ISP.

Some ISPs use the MAC address from your Network Interface Card (NIC) to identify you on their network. A MAC address is the ID of a network device that allows other devices or computers to verify authenticity.
If your ISP requires this, you will need to clone the MAC address of your computer's NIC, which will allow the Wireless MAXg Router to take that MAC address and use it in the place of its own MAC address for network identification.
To determine the MAC address of your NIC, perform the following steps:
Windows XP, 2000, or NT Users: Click Windows Start and then Run. Type cmd and click OK. At the DOS prompt, type ipconfig /all. You will see all of the information regarding your network connection. The MAC address may be listed as the Physical Address.
Windows Me, 98, or 95 Users: Click Windows Start and then Run. Type winipcfg and click OK. You will see all of the information regarding your network connection. The MAC address may be listed as the Physical Address.
Open the Client Devices drop-down menu in the Web User Interface and select the MAC address for your computer's NIC and then click Save at the bottom of the page.
If the correct MAC address is not listed, you can enter it manually and click Save at the bottom of the page.
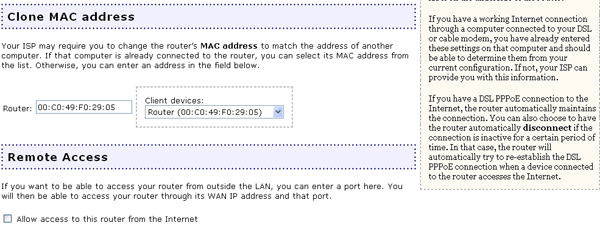
If you select this option, you will be able to access the Wireless MAXg Router from a remote location over the Internet and change any of the configuration settings. Enabling Remote Access creates a security risk. However, you can reduce the risk by creating a user name and password that would be difficult for an intruder to determine. You can change the user name and password on the Security page.

You will need to enter a port to be opened so that you can access the router. After selecting a port and saving your changes, you can enter the Remote Address that is provided in order to enter the Web User Interface from any location. Depending on the port you select, an example of the Remote address would be http://167.1.0.24:8080
If you successfully connect, you will be prompted for your user name and password to continue accessing the router.
Note: The Remote address must be entered exactly as it is seen in your Web User Interface or you will not be able to access the router remotely.
If you make a physical connection from the Wireless MAXg Router’s WAN port to an existing network or networks, you may need to establish Static Routes. This will allow the router to use its own network address, which is different from the network to which it is connected. This will also allow the router to connect to specific networks that already exist on the WAN side.
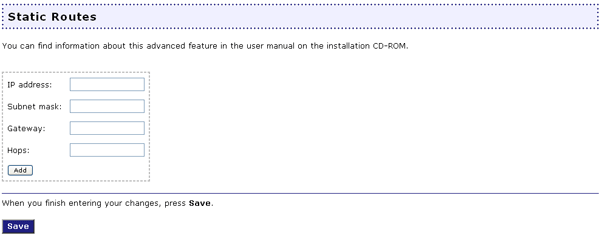
Each available network will need to have their own IP network address in the IP address field. They will then need to enter the Subnet mask. The IP address of the other router will need to be entered in the Gateway field. Lastly, you will need to enter the amount of Hops your router must make in order to connect to the other network. The amount of hops that must be made is determined by how many routers are between your MAXg Router and the respective network. For example, if there is another router connected to the Wireless MAXg Router's WAN port, then there is one hop between the MAXg Router's WAN port and any client connected to the second router.
Some ISPs will provide you with a user name and password for your PPPoE account. If you have these, enter them in the appropriate fields in this section.
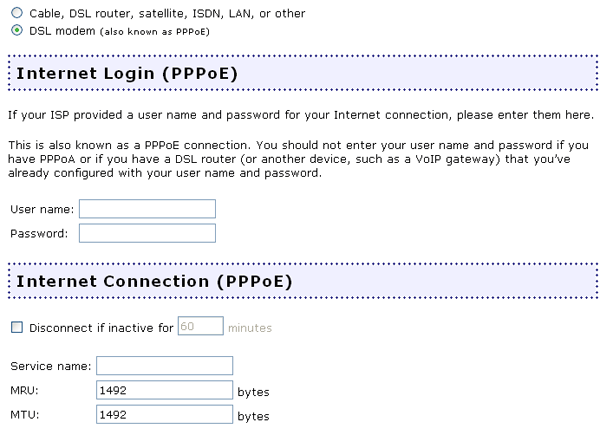
In this section you can set specific details regarding your PPPoE connection. First, you can select the checkbox for Disconnect if inactive for. You will then need to specify a timeframe. Selecting and setting a timeframe will cause your Internet connection to be disconnected if your Internet connection is not active for the amount of time you specified.
Next you can specify the PPPoE Service Name. The PPPoE Service Name is an ISP name or a class of service that is configured on the PPPoE server. You can contact your ISP to get the PPoE Service Name.
You can also change the values for the MRU and for the MTU.
The MRU is the largest packet size the router will allow a computer on the network to receive. MRU stands for Maximum Receive Unit. Contact your ISP if you have any questions regarding what this number should be or if it is necessary. If your ISP does not instruct you to change this number, leave the default setting of 1492.
The MTU is the largest packet size the router will allow a computer on the network to send. MTU stands for Maximum Transmission Unit. Contact your ISP if you have any questions regarding what this number should be or if it is necessary. If your ISP does not instruct you to change this number, leave the default setting of 1492.

If your ISP gave you a Host Name for your Internet connection, enter it here. The Host Name is not the same as your User Name. If you have any questions about if you need a Host Name or what it may be, contact your ISP.
Some ISPs use the MAC address from your Network Interface Card (NIC) to identify you on their network. A MAC address is the ID of a network device that allows other devices or computers to verify authenticity.
If your ISP requires this, you will need to clone the MAC address of your computer's NIC, which will allow the Wireless MAXg Router to take that MAC address and use it in the place of its own MAC address for network identification.

To determine the MAC address of your NIC, perform the following steps:
Windows XP, 2000, or NT Users: Click Windows Start and then Run. Type cmd and click OK. At the DOS prompt, type ipconfig /all. You will see all of the information regarding your network connection. The MAC address may be listed as the Physical Address.
Windows Me, 98, or 95 Users: Click Windows Start and then Run. Type winipcfg and click OK. You will see all of the information regarding your network connection. The MAC address may be listed as the Physical Address.
Open the Client Devices drop-down menu in the Web User Interface and select the MAC address for your computer's NIC and then click Save at the bottom of the page.
If the MAC address for your NIC is not listed, you can enter it manually and click Save at the bottom of the page.
If you select this option, you will be able to access the Wireless MAXg Router from a remote location over the Internet and change any of the configuration settings. Enabling Remote Access creates a security risk. However, you can reduce the risk by creating a user name and password that would be difficult for an intruder to determine. You can change the user name and password on the Security page.

You will need to enter a port to be opened so that you can access the router. After selecting a port, you can enter the Remote Address that is provided to enter the Web Interface from any location. Depending on the port you select, an example of the Remote address would be http://167.1.0.24:8080
If you successfully connect, you will be prompted for your user name and password to continue accessing the router.
Note: The Remote address must be entered exactly as it is seen in your Web User Interface or you will not be able to access the router remotely.
If you connect the Wireless MAXg Router to an existing network as the primary gateway to the Internet or connect another router to the Wireless MAXg Router, you may need to establish Static Routes. This will allow the clients that are not directly connected to the Wireless MAXg Router to access the Internet.

Each available network will need to have their own IP network address in the IP address field. They will then need to enter the Subnet mask. The IP address of the other router will need to be entered in the Gateway field. Lastly, you will need to enter the amount of Hops your router must make in order to connect to the other network. The amount of hops that must be made is determined by how many routers are between the client and the Wireless MAXg Router. For example, if an individual client is connected to a router, which is in turn connected to the Wireless MAXg Router, it will take two hops to access the Wireless MAXg Router.
After making any changes to the configuration options or security settings of the Wireless MAXg Router, you must click Save in order for your changes to be saved and implemented.
If your Internet Service Provider (ISP) uses a PPTP connection, select the My ISP uses a PPTP connection checkbox. If you have any questions regarding any of the connection settings, contact your ISP.
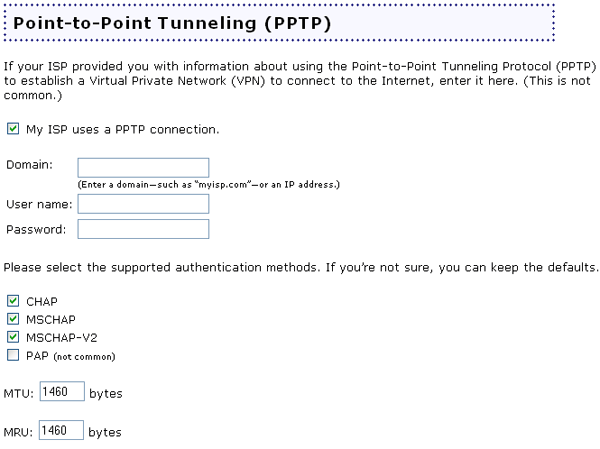
The first thing you will need to enter is the Domain. This is either the Internet name of your ISP or the IP address that you will use to connect to the Internet. Examples would be either myisp.com or 123.45.678.9
You will need to enter your User name and Password for your ISP account, which your ISP assigned to you or which you chose for your account.
If your ISP uses a specific authentication method, you will need to select the appropriate type or types. The choices are CHAP, MSCHAP, MSCHAP-V2, or PAP. Your ISP will inform you if you need to enable or disable any of these authentication methods. If your ISP has not mentioned any specific types of authentication and you are unsure about what type of authentication your ISP uses, you can leave the default settings.
CHAP stands for Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol. This is a type of authentication protocol in which the server sends the client a key to be used to encrypt the user name and password. CHAP requires the client to authenticate itself at the beginning of a session and at regular intervals during the session to make sure that the client hasn't been replaced by an unauthorised intruder, for instance by switching phone lines.
MSCHAP stands for Microsoft Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol. This is very similar to CHAP in how it works, but it is in a format designed specifically for compatibility with Windows NT and 95. The MSCHAP format also does not require the authenticator to store a clear-text or reversibly encrypted password. One more difference is that MSCHAP defines an extended set of codes that are returned in a Failure packet when a connection is denied.
MSCHAP-V2 is simply the second version of MSCHAP and it includes more security features and fixes some of the oversights that were discovered in the original MSCHAP.
PAP stands for Password Authentication Protocol. This type of authentication is a very simplified method since it is simply verifying the password, so the security level is relatively low. This is not a very common form of authentication anymore because of the newer methods that offer a higher level of security.
The last thing you may need to change is the MTU and MRU values. MTU stands for Maximum Transmit Unit and MRU stands for Maximum Receive Unit. These control the maximum size of packets that are sent and received over your PPTP connection. Your ISP may give you different amounts to enter for these settings in order to control bandwidth traffic.
When you are finished, click Save. The router will restart and you should then have an Internet connection. You can go to the Status page to view your connection information.