Advanced Setting
 |
The Advanced Setting menu gives you the following options:
- System Time determines how your local area network's system time is set.
- System Log determines the destination of the system log.
- Dynamic DNS (DDNS) lets you assign the IP address of your host computer dynamically.
- SNMP lets you manage your LAN remotely.
- Routing lets you define paths for outgoing data packets.
|
System Time
The System Time option lets you set your local area network's time of day manually or obtains the time from either a time server or the PC that is running the router's Web User Interface.
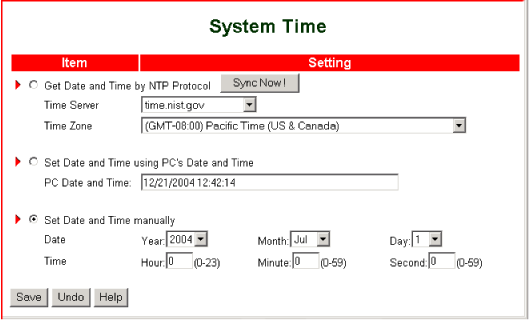
Select one of the following options by clicking the radio button to the left of the option. Then make your option-specific selections.
- Get Date and Time by NTP Protocol—Retrieves the time of day from a time server. To use this feature:
- Select a Time Server from the drop-down list.
- Select your Time Zone from the drop-down list.
- Click Sync Now ! to set your network's time of day.
- Set Date and Time using PC's Date and Time—Retrieves the time of day from the administrator host machine that is currently running the router's Web User Interface.
- Set Date and Time manually—Lets you enter the date and time.
After making any changes, remember to click Save.
System Log
The System Log option lets you direct the system log to an IP address, specific email addresses, or both.
To send the log after specifying the destination in the System Log screen:
- Click View Log.
- On the System Log display screen, click Download.
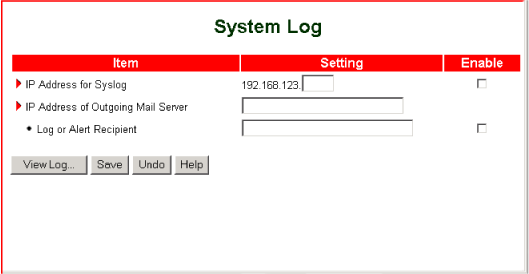
- IP Address for Syslog—The IP address to receive the log.
Enable—If this box is checked, the IP address receives the log. If this box is not checked, the IP address does not receive the log.
- IP Address of Outgoing Mail Server—The SMTP server IP address and port, for example, 192.168.1.100:26. If you specify the IP address only, for example, 192.168.1.101, the router uses the default port value of 25.
- Log or Alert Recipient—The SMTP mail recipient, for example, your_name@your_isp.com
Enable—If this box is checked, the email recipient receives the log. If this box is not checked, the email recipient does not receive the log.
- View Log—Displays the system log.
Dynamic DNS
To host your server on a changing IP address, you must use Dynamic DNS (DDNS) to allow access based on your host name rather than your address.
To use this feature, you must first register with a DDNS provider that is on the Dynamic DNS screen's preset Provider list.
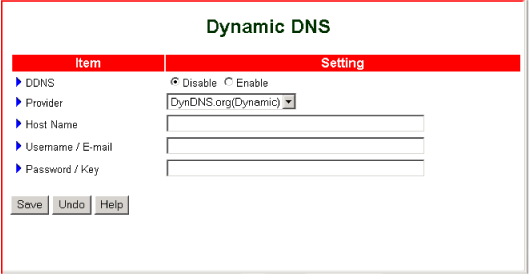
- DDNS—Disable turns DDNS off. Enable turns DDNS on.
- Provider—Select the name of the DNS with which you are registered.
- Host Name—Type your host name.
- Username / E-mail—Enter your user name as registered with your DDNS provider.
- Password / Key—Enter your password as registered with your DDNS provider.
After making any changes, remember to click Save.
SNMP
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) gives you a measure of remote network control by letting you monitor events on your network through an SNMP software application.
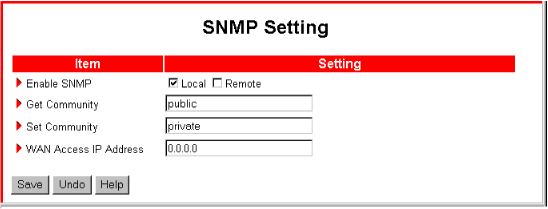
- Enable SNMP
- Local—Enables the router to respond to SNMP requests from the LAN.
- Remote—Enables the router to respond to SNMP requests from the WAN.
- Get Community—The name of the community to which the router will respond to information queries.
- Set Community—The name of the community that the router will allow to set SNMP information.
- WAN Access IP Address—The IP address that is allowed SNMP access to the router.
To disable SNMP, clear both Local and Remote.
After making any changes, remember to click Save.
Routing
Routing lets you determine which physical interface address to use for outgoing IP data. If you have more than one router, you must enable routing in order for packets to find the proper path for communication between subnets.
The Routing Table sets up static routing with up to eight routing rules, or paths.
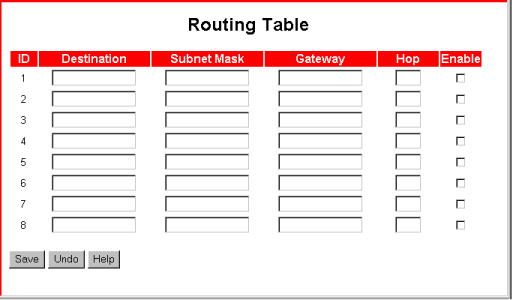
Each rule specifies a path between the router and a subnet. When a rule is enabled, devices connected to the router can communicate with devices on the subnet. To specify a routing rule, you must provide the following information:
- Destination—IP address of the destination subnet.
- Subnet Mask—Subnet mask of the destination subnet.
- Gateway—IP address of the subnet's gateway device.
- Hop—The count of routing devices between the router and individual computers (or other resources) on the destination subnet. For example, if a computer is connected to a gateway that is directly connected to your router, a data packet originating on your LAN would have to make one hop to reach the subnet and could then reach the computer.
- Enable—When this box is checked, the routing rule is applied. When this box is not checked, the routing rule is not applied.





