Contents:
About the 802.11g Wireless Turbo PC Card, PCI Adapter, and Access Point
Network Configuration and Planning
Adapter Installation and Configuration for Windows 98 SE/2000/Me/XP
802.11g Wireless Turbo Configuration Utilities
Product Specifications for 802.11g Wireless Turbo PC Card and PCI Adapter
Product Specifications for 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point
802.11g Wireless Turbo PC Card, PCI Adapter, and Access Point User Guide
802.11g Wireless Turbo Configuration Utilities
802.11g Wireless Turbo PC/PCI Network Configuration Utility
802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point Configuration Utility
802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point Web Configurator
802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point Telnet Configuration
802.11g Wireless Turbo PC/PCI Network Configuration Utility
The following section describes the various functions of the Network Configuration Utility. This utility provides quick access to all adapter settings. The configuration settings will be set by default to the correct values. Only advanced users should change any of the following settings.
After installation is complete, a Utility Tool icon will appear in the taskbar on the right side near the clock. Double-clicking the icon in the Quick Launch bar will open the Utility Tool main menu, providing quick access to all adapter settings. The Configuration Utility icon will be colored to indicate the status of your wireless network: red for disconnected, yellow for roaming, and green for connected with good quality.
![]()
![]()
![]()
There are five sections to the LAN Configuration Utility: Link Information, Configuration, Security, Site Survey, and About.
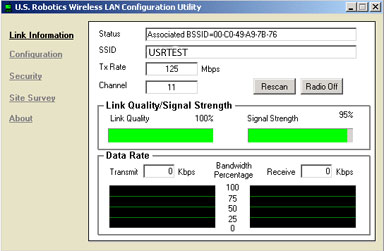
Link Information:
The Link Information section provides information about the current wireless network connection. You will see the status of the network, the SSID, the Tx Rate, and the Channel. There are two graph bars that represent the Link Quality and the Signal Strength. There are also two graphs that represent the Transmit and Receive Data Rates.
There are two buttons on this screen: Rescan and Radio Off. Click Rescan to search the area for available wireless networks. Click Radio Off to disable the wireless funcitionality.
Configuration:
In the Configuration section you can change the network configuration information for the 802.11g Wireless Turbo PC Card or PCI Adapter.
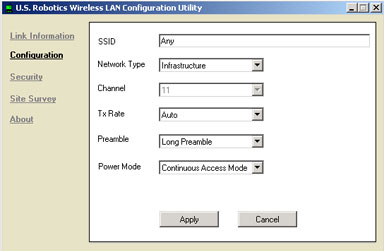
Description of Settings
The following are explanations of each adapter setting in the Configuration section.
SSID: SSID (Service Set Identifier) is the unique name that is shared among all 802.11g Wireless Turbo PC Cards or PCI Adapters and 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Points in a wireless network. The SSID must be identical for all 802.11g Wireless Turbo PC Card or PCI Adapters and 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Points participating in the same network. The SSID is case sensitive and must not exceed 30 characters.
Network Type:
- AdHoc: This mode is used for a simple peer-to-peer network.
This type of network only allows the sharing of local resources between
wireless clients without a Wireless Access Point.
Note: If you want this type of connection, the WPA-PSK option for security encryption will not be available. You will need to select a different type of security authentication.
- Infrastructure: This mode allows a wireless LAN to be integrated into an existing wired network through a Wireless Access Point. Infrastructure type networks also permit roaming between Wireless Access Points.
- Auto-Detect: This mode will allow your 802.11g Wireless Turbo
PC Card or PCI Adapter to scan and connect to any local wireless network,
either AdHoc or Infrastucture.

Channel: This setting specifies the 802.11g channel used by the Wireless LAN to communicate. In an Infrastructure network, clients will scan all available channels and identify SSIDs to connect to. Channel and WEP info is also provided by the Access Point.
- Changing the Channel: In Infrastructure networks, channel selection is done on the Access Point. Networks that are operating in Infrastructure mode automatically scan for a channel. The following table contains the operational channel frequency for several countries.
|
Regulatory Channel Frequency
|
|||||
|
Channel
|
Frequency (MHz)
|
FCC
|
Canada
|
ETSI
|
Japan
|
|
1
|
2412
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
|
|
2
|
2417
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
|
|
3
|
2422
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
|
|
4
|
2427
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
|
|
5
|
2432
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
|
|
6
|
2437
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
|
|
7
|
2442
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
|
|
8
|
2447
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
|
|
9
|
2452
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
|
|
10
|
2457
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
|
|
11
|
2465
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
|
|
12
|
2467
|
|
|
X
|
|
|
13
|
2472
|
|
|
X
|
|
|
14
|
2484
|
|
|
|
X
|
Tx Rate: Tx Rate (transmit rate) selects the allowable transfer rates of the 802.11g Wireless Turbo PC Cards or PCI Adapters. To optimize performance and range, the Tx Rate should be set to Fully Automatic. This will automatically adjust the transfer speed for the best performance and longest range.
Note: The Tx rate can only be set if the 802.11g Wireless Turbo PC Cards or PCI Adapters are in Infrastructure mode.

Note: In order to connect at the desired TX rate, the device you are connecting to needs to both support and be available at that rate.
Preamble: The preamble can be set to either Long Preamble or Short Preamble.
Power Mode: Power Mode enables or disables the power saving features of your wireless adapter. When enabled on a laptop, the power saving mode can reduce power consumption by the wireless PC card and extend the battery life of your laptop.
Note: The Power Mode is set by default to Continuous Access Mode. To change the setting, select either Maximum Power Save or Fast Power Save from the drop-down list and click Apply.
Security:
Within this section, you can change the security settings of your 802.11g Wireless Turbo PC Card or PCI Adapter.

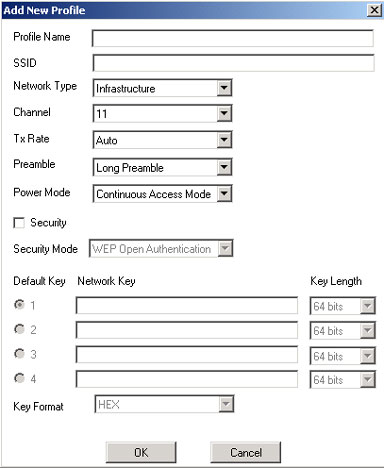
You can enable Security by selecting the checkbox at the top of the screen. If you select this, you will then need to enter a Network Key. You will need to select either HEX or ASCII in the Key Format dropdown menu.
You can change the authentication mode by selecting the drop-down menu next to Security Mode. You can select from WEP Open Authentication, WEP Shared Authentication, WPA, WPA-PSK, or CCX.

WEP is an encryption scheme that is used to protect your wireless data communications. WEP uses a combination of 64-bit keys, 128-bit keys, or 256-bit keys to provide access control to your network and encryption security for every data transmission. To decode a data transmission, each wireless client on the network must use an identical 64-bit, 128-bit, or 256-bit key.
WPA’s use of keys is very similar to WEP, but the key is only used once to start the process. Once communication is established, the key will randomly change. This provides a higher level of security. It is recommended that you use the most secure mechanism available on your 802.11g Wireless Turbo PC Card or PCI Adapter.
Note: WPA and WPA-PSK can only be used if the wireless network you want to connect to is capable of employing WPA or WPA-PSK as an authentication mode. Many older wireless devices may not be able to use WPA or WPA-PSK, so this should be verified before WPA or WPA-PSK is selected. Non-matching authentication modes will keep you from being able to connect to a wireless network.
If you enable WEP encryption, you will need to select and enter the WEP Network Keys from one to four, and you will need to select the Key Length from 64 bits, 128 bits, or 256 bits.
If you enable WPA, you will need to enter a User Name and supply a Certificate of Authority. These will be supplied to you by your network administrator. By default, EAP-TLS is the only option for the Protocol. EAP-TLS stands for Extensible Authentication Protocol - Transport Layer Security. EAP-TLS is an authentication method that requires both the client and the server to prove their identities to each other.

If you enable WPA-PSK, you will need to enter a Passphrase and then enter it again to confirm it. This passphrase must be the same on each computer that is connected to the wireless network.

If you enable CCX, you can select either EAP-TLS or LEAP for the Protocol. EAP-TLS is an authentication method that requires both the client and the server to prove their identities to each other. LEAP stands for Lightweight Extensible Authentication Protocol. LEAP is a Cisco-based authentication method that requires both a user name and password to be shared between the wireless client and the server. If you select EAP-TLS, you will need to enter a User Name and supply a Certificate of Authority. These will be supplied to you by your network administrator. If you select LEAP, you will need to enter the User Name and Password that your network administrator will provide to you.

Site Survey:
Within this section, you can view the other networking products that you can connect to.

There are two ways to connect with a wireless networking product in the list: either select a wireless networking product and click Connect or double-click a wireless networking product to automatically connect to it. Click Refresh to update the information that is shown.
If you click Advanced, you can specify what type of network your wireless network product primarily searches for. If you want to only search for other wireless cards, select Ad-Hoc Only. If you want to search for Access Points or Wireless Routers in Infrastructure mode, select AP Only. If you want to search for any type of wireless network, select Both. By default, this is set to Both.
In the Profile area, you can create, remove, or edit the information for networking profiles. You can also connect to a profile you have created. Different networking profiles can be used to save specific configuration information for different situations or areas, without needing to re-enter all of the information each time. If you select a profile and click Connect, you will establish a connection to the network specified in the profile, if it is accessible. If you select a profile and click Properties, you can view the settings information for that profile and make any changes.
About:
Within this section you can view the version information for your 802.11g Wireless Turbo PC Card or PCI Adapter.

802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point Configuration Utility
![]()
The Configuration Utility for the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point has seven sections: Link Information, AP Settings, IP Settings, WEP Settings, 802.1X Settings, Tools, and MAC Filter Settings. If you make any changes to the configuration information within any of the six sections, you must click Apply in order for the changes to take effect. You will be prompted for your user name and password each time you change and apply a setting. The default user name is admin. There is no default password. If the changes do not appear or if the information shown is not correct, click Refresh to update the information that is shown.
Link Information
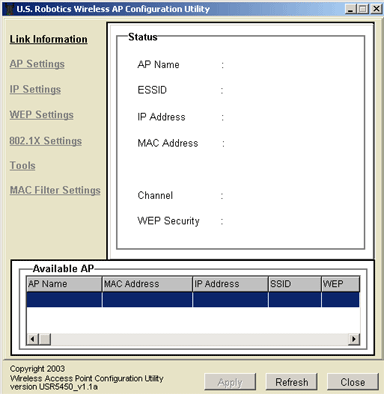
Within the Status area, you can view information about the AP Name, the ESSID, the IP Address, the Mac Address, the Domain, the Channel, and the WEP Security.
In the Available AP area, you can see a list of all the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Points that are detected.
Note: On any screen, you can double-click the listing for a device in the Available AP area and the Web Configuration Utility will launch in a new Web browser window.
AP Settings
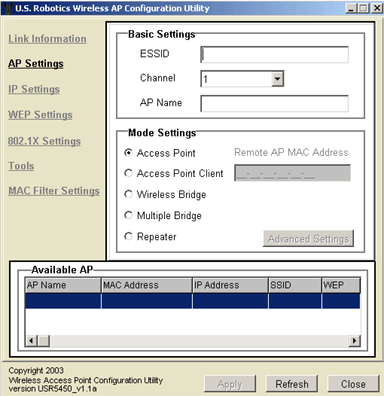
Within the AP Settings section, there are three areas: Basic Settings, Mode Setting, and Available AP.
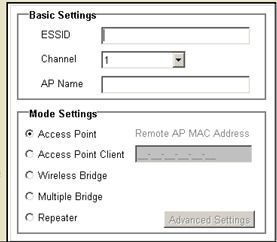
In the Basic Settings area, you can enter an ESSID, select a channel, and assign a name to the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point.
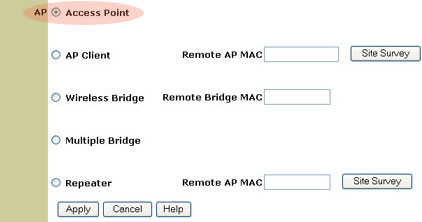
For Mode Setting, you can choose from the following:
- Access Point mode
- Access Point Client mode
- Wireless Bridge mode
- Multiple Bridge mode
- Repeater mode
Note: If you select either Access Point Client mode or Repeater mode, you will need to enter the Remote AP MAC Address. If you set the Remote AP MAC Address to all zeros, which is a generic setting, the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point will associate with any available client.
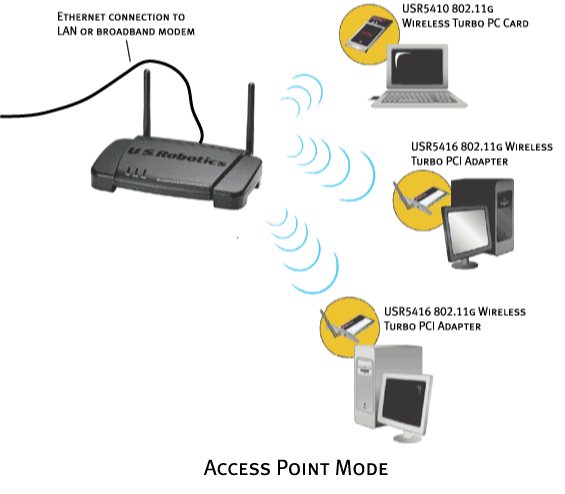
Access Point mode
Access Point mode is used to connect up to 20 wireless clients. If you have up to 20 computers, each equipped with a wireless adapter, you can use Access Point mode to create a wireless network among the computers. This is the simplest configuration mode for the Wireless Access Point.
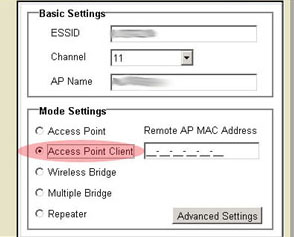
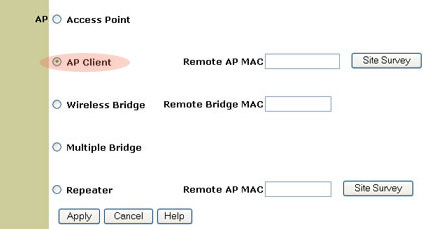
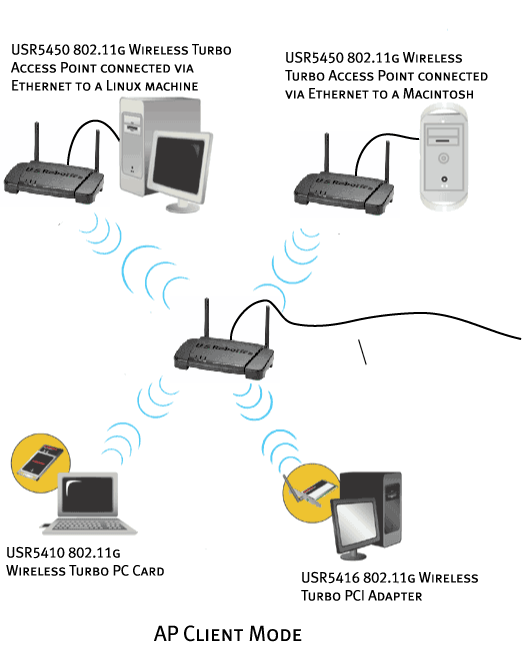
Access Point Client mode
Access Point Client mode is used to connect any computers that don't support wireless adapters. By connecting a Wireless Access Point to each of these machines via Ethernet, the Wireless Access Point can be used as a wireless adapter. An example of this would be if you had four computers not all using the same operating platform: two of them running Windows 2000 with wireless adapters installed, one running Mac OS9, and one running Linux. If you connect a Wireless Access Point to the Macintosh computer, one to the Linux computer, and one for both Windows computers, and then set each Wireless Access Point to Access Point Client mode, you could wirelessly network each of these computers together.
Note: If your Ethernet device or network adapter does not support auto-switching, you may need to use an Ethernet crossover cable to connect the Wireless Access Point in Access Point Client mode. Refer to the documentation for your Ethernet device or network adapter to see if it supports auto-switching. The USRobotics Wireless Turbo Multi-Function Access Point supports auto-switching.
Note: If you select Access Point Client mode, you will need to enter the MAC address for the remote Access Point.
- Select Advanced Setting on the HTML page.
- Click to select AP Client.
- Enter the LAN Hardware Address of the Router or Access Point to which
you wish to connect. Click Apply at the bottom of the screen.
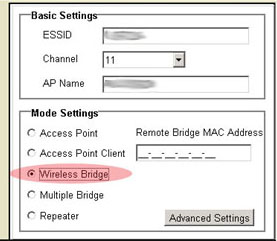
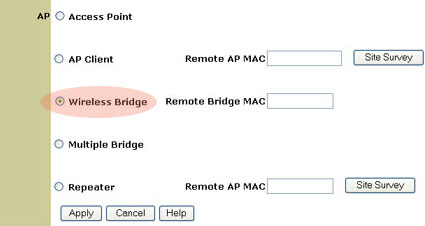
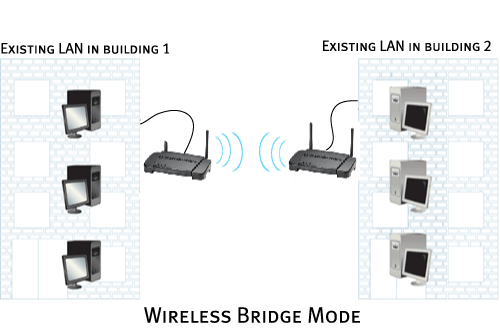
Wireless Bridge mode
Wireless Bridge mode is used to wirelessly connect two existing wired Local Area Networks (LANs). By connecting a Wireless Access Point to each LAN and selecting Wireless Bridge mode, the two Wireless Access Points will talk only with each other, creating a secure connection between the different networks.
Note: If you select Wireless Bridge mode, you will need to enter the MAC address for the remote Wireless Bridge.
- You will be bridging two Access Points together; we will refer to them as Access Point 1 and Access Point 2.
- On Access Point 1, select Advanced Setting on the HTML page.
- Click to select Wireless Bridge.
- Enter the LAN Hardware Address of Access Point 2.
- Click Apply at the bottom of the screen.
- On Access Point 2, select Advanced Setting on the HTML page.
- Click to select Wireless Bridge.
- Enter the LAN Hardware Address of Access Point 1.
- Click Apply at the bottom of the screen.
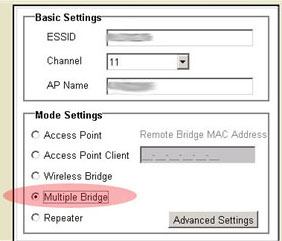
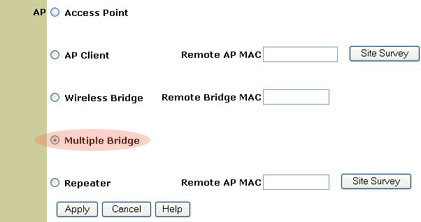
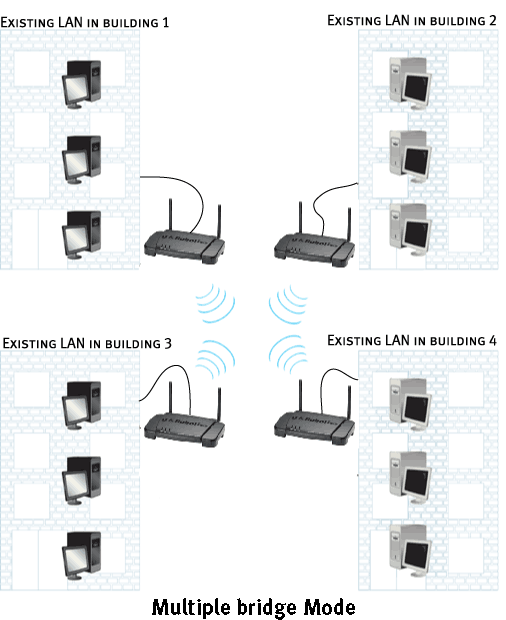
Multiple Bridge mode
Multiple Bridge mode is similar to Wireless Bridge mode, but it is used when you want to wirelessly connect more than two wired LANs. By connecting a Wireless Access Point to each LAN and selecting Multiple Bridge mode, the multiple Wireless Access Points will talk only with each other, creating a secure connection between the different networks.
- Make sure all Access Points to be bridged are set up identically: same channel, same SSID, same modulation, and same encryption.
- Select Advanced Setting on the HTML page.
- Click to select Multiple Bridge.
- Click Apply at the bottom of the screen.
- After the individual Access Points reboot, connect them to appropriate
switches or computers depending on your implementation.
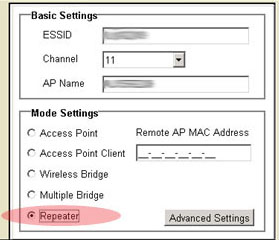
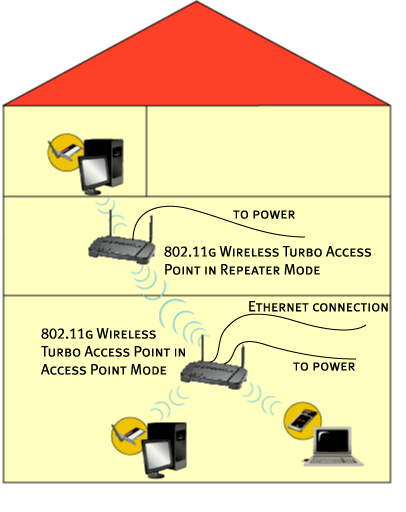
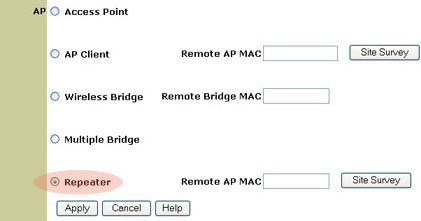
Repeater mode
If you have a wireless client that is positioned in your home or office and the transmission signals are weakened, you can use a 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point to boost the signal to and from the wireless clients. By placing the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point between the two clients and selecting Repeater mode, the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point will then fill in the gap in the transmission capabilities and pass any network information between the wireless clients.
To use a 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point in Repeater mode, you must first configure the Access Point using an Ethernet connection. After the Access Point has been configured for Repeater mode, remove the Ethernet connection, position the Access Point in the proper location, and plug in the power supply.
Note: Use the Ethernet cable to configure the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point for Repeater mode. Once configured, the Ethernet cable is not used.
- Select Advanced Setting on the HTML page.
- Click to select Repeater.
- Enter the LAN Hardware Address of the Router or Access Point from which you wish to repeat.
- Click Apply at the bottom of the screen.
- If you wish to set up additional USR5450 Access Points as repeaters,
follow the above instructions for each one, replacing the LAN MAC address
for the device from which you wish to repeat.
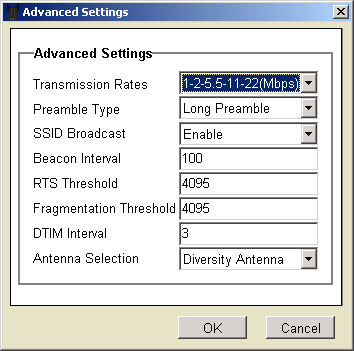
In the Mode Setting area there is also the Advanced Setting button. Here you will have eight options for which you can enter information: Transmission Rates, Preamble Type, SSID Broadcast, Beacon Interval, RTS Threshold, Fragmentation Threshold, DTIM Interval, and Antenna Selection.
- For Transmission Rates, you can select 1-2 (Mbps), 1-2-5.5-11 (Mbps), 1-2-5.5-11-22 (Mbps), or 1-2-5.5-11-22-54(Mbps).
- In Preamble Type, you can select either Short Preamble or Long Preamble.
- In SSID Broadcast, you can select either Enable or Disable.
It is recommended that you select Disable to increase the security
of your network and that you change the SSID from the default. The SSID
is case-sensitive.
Note: If you disable SSID Broadcast, the correct information must be manually entered for each wireless client that needs to be connected to your wireless network. With SSID Broadcast disabled, wireless clients will not be able to scan and connect automatically to your wireless network.
- Beacon Interval, RTS Threshold, Fragmentation Threshold, and DTIM Interval are set at the optimal levels by default. They should only be reconfigured by advanced users. Incorrect configuration can seriously limit the performance of your device.
- In Antenna Selection, you can select either Left Antenna, Right Antenna, or Diversity Antenna.
When you are done selecting or entering any information, click OK to return to the main screen.
In the Available AP area, you can see a list of all the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Points that are detected.
IP Settings
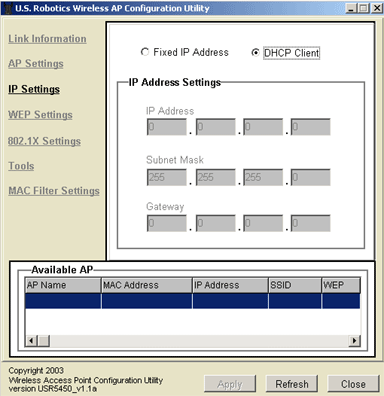
In the IP Settings section, you can select either Fixed IP Address or DHCP Client.
If you select DHCP Client, this information will be retrieved automatically. The Configuration Utility is set to DHCP Client by default.
Note: If you are not connected to an adapter or device that supports DHCP, the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point will not obtain an IP Address. Without an IP Address, the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point will still pass wireless network traffic between clients, but you will not be able to configure any of the settings using the HTML utility.
If you select Fixed IP Address, you will then need to enter the following information: an IP Address, a Subnet Mask, and a Gateway.
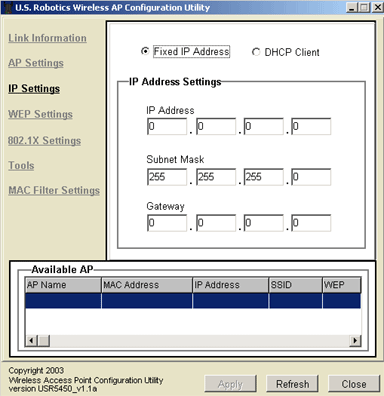
In the Available AP area, you can see a list of all the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Points that are detected.
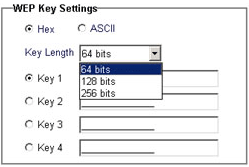
WEP Settings
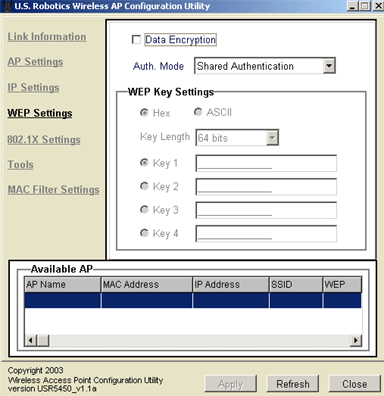
You can change the authentication mode by selecting the drop-down menu next to Auth. Mode. You can select from Auto Switch, Open Authentication, or Shared Authentication.
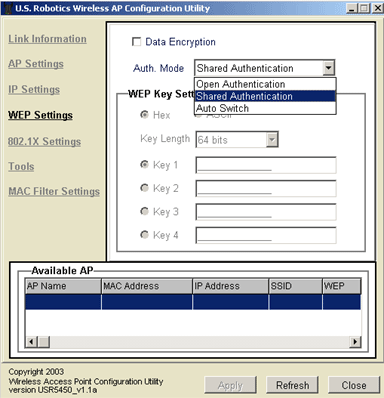
In the WEP Settings section, you can enable Data Encryption by selecting the checkbox at the top of the screen. You will also need to select either HEX or ASCII in the WEP Key Setting window.
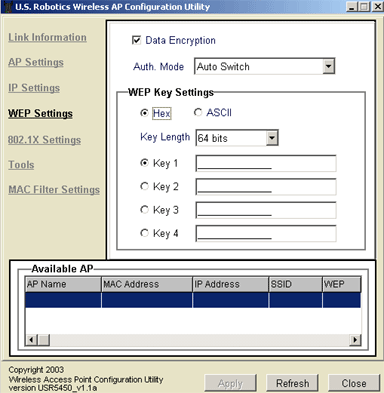
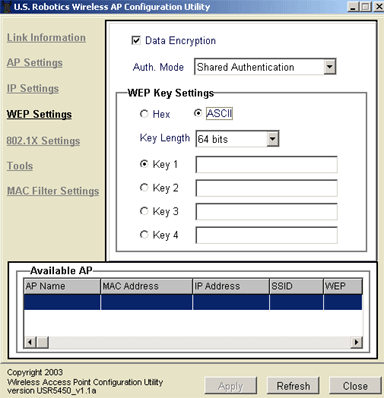
You will also need to select and enter up to four WEP Keys, and you will need to select the Key Length from 64 bits, 128 bits, or 256 bits.
In the Available AP area, you can see a list of all the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Points that are detected.
Note: When 802.1X is enabled on your Access Point, you should select a maximum of 128 bit WEP encryption. Windows clients that have 802.1X enabled may not be able to take advantage of the 256 bit WEP encryption.
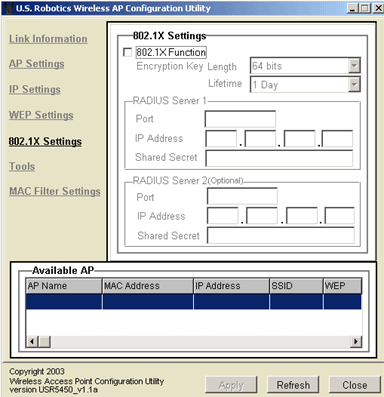
802.1X Settings
In the 802.1X Settings area, you can configure the 802.1X functions.
Note: If the Configuration Utility detects an Access Point that is not enabled for 802.1X, it is required that the firmware on that Access Point be updated. For the latest version of the firmware, please visit www.usr.com/support
Note: If your 802.1X wireless clients are on a Microsoft network, WEP must be enabled.
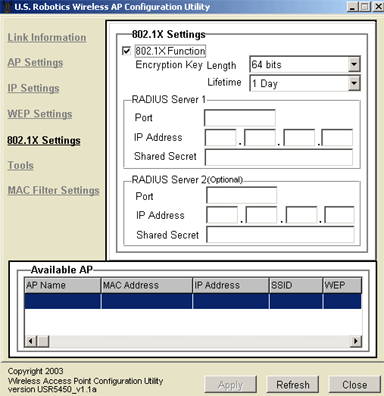
To enable 802.1X, select the box next to 802.1X Function.
You will then need to provide the information for RADIUS Server 1. This is the computer to which the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point creates a secure connection. You will need to supply the IP Address of the RADIUS Server. You also need to supply a Port number for the RADIUS Server or use the default 1812. You will then need to provide the IP Address for the computer to which you are connecting. Next, you will need to provide the Shared Secret. This can be a word or a set of numbers and will be used as an additional form of security. Each 802.1X wireless client that will connect to the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point must have the correct Shared Secret or the Access Point will be denied.
The use of RADIUS Server 2 is optional. These fields are used to enter the information for a backup server. If the server computer identified in RADIUS Server 1 is not working or does not respond, RADIUS Server 2 can be used so that you still have WLAN access.
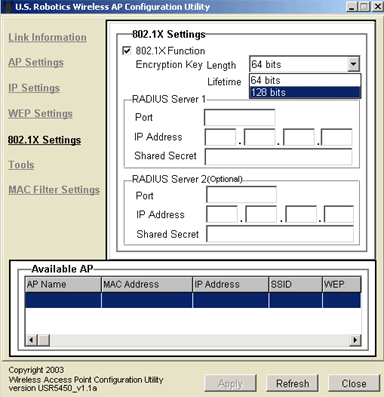
If you enable 802.1X, you will need to select an Encryption Key Length. You can choose either 64 bits or 128 bits. This will determine the level of encryption between the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point and the RADIUS Server. This does not set the level of WEP encryption for the WLAN.
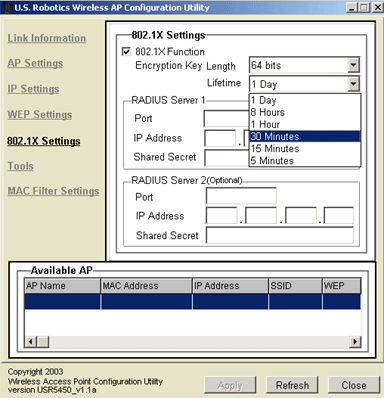
You will then need to select the Lifetime of the encryption. You can choose 5 Minutes, 15 Minutes, 30 Minutes, 1 Hour, 8 Hours, or 1 Day. This will determine how long the encryption will remain in effect.
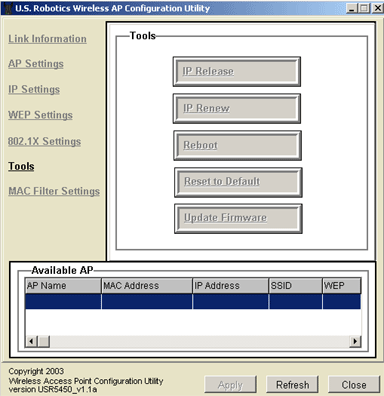
Tools
Within the Tools area, there are five options: IP Release, IP Renew, Reboot, Reset to Default, and Update Firmware.
If you need to release the IP Address of the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point, click IP Release.
If you need renew the IP Address of the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point, click IP Renew.
If the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point stops responding, click Reboot and the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point will restart.
If you need to restore the original settings of the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point, click Reset to Default.
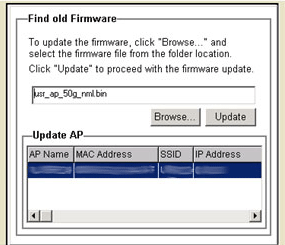
If you download any new firmware upgrades, click Update Firmware to implement the update.
Note: In order to update the firmware, which uses TFTP, the Access Point needs a valid IP Address. It will not upload with an address of 0.0.0.0.
Click Browse to locate the new firmware file that you downloaded. When you locate the file, click Update.
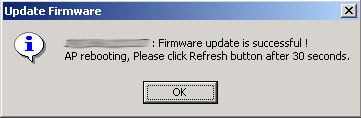
After the firmware is updated, click OK.
Note: If the Firmware Update fails, verify that you have an IP Address. If you do not have an IP Address, you will not be able to update the firmware.
MAC Filter Settings
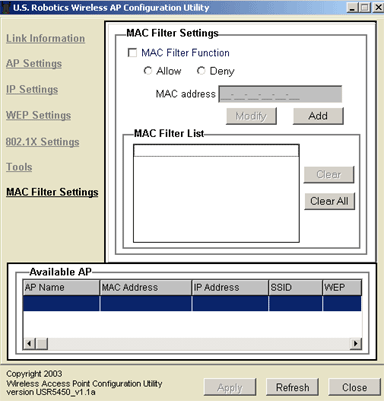
You can either enable or disable the MAC filter by selecting or deselecting the checkbox next to MAC Filter Function. If you enable the MAC Filter, you will need to select either Allow or Deny for each entry you create in the Filter List. If you create an entry and select Allow, that wireless client will be permitted to access the resources on your wireless network. If you create an entry and select Deny, that wireless client will not be allowed to access the resources on your wireless network. You can remove an entry from the MAC Filter List by selecting it and then clicking Clear, or you can remove the entire list by clicking Clear All. Click Apply to save your changes.
Note: Before you click Clear All, be sure to clear the MAC Filter Function checkbox, or you will deny access to all wireless clients on your network.
802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point Web Configurator
After launching the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point Configuration Utility, note the IP address of the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point. Double-click the Access Point in the Available AP list. This will launch the Web Configurator of the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point.
There are seven sections to the Web Configurator: Status, Basic Setting, IP Setting, Advanced Setting, Security, and Tools. Every time you make a change to the configuration settings of the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point, you must click Apply for the changes to take effect.
Status
Within Status, you can view the current network information for the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point. Click Refresh to update the information that is shown.
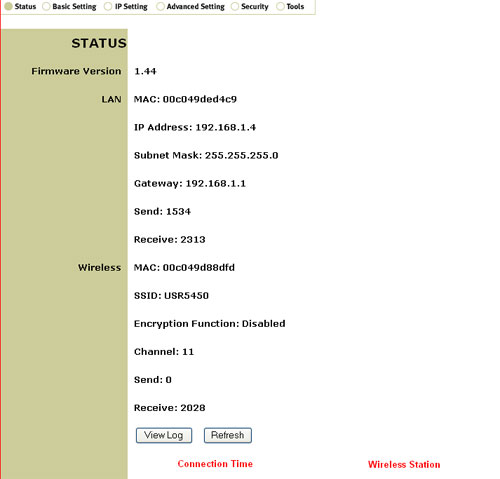
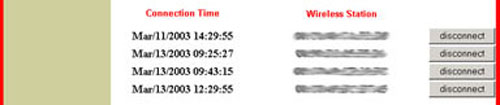
At the bottom of the Status screen you can see the wireless clients that are connected to the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point. Next to each client listing will be a disconnect button. If you click disconnect, you will be prompted to enable the MAC filter option. Go to the Security screen, click Enable for the MAC Filter, and then select Only deny PCs with MAC listed below to access device. If you then return to the Status page and click disconnect for a client, that client's MAC Address will be added to the MAC Filter list on the Security page and that client will not be allowed to access your wireless network. You will need to save and apply changes and then reboot your computer for the changes to take effect.
Basic Setting
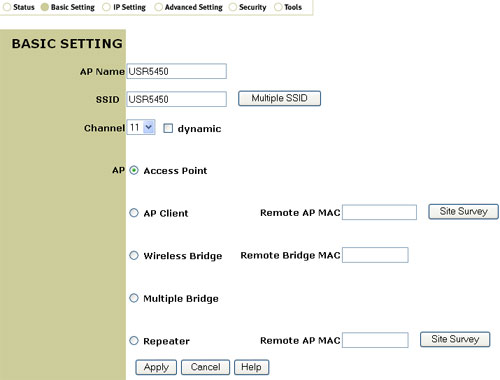
In this section you can assign a name to the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point, enter an SSID, and select a channel. If you select the checkbox next to dynamic, an available channel will automatically be selected.
Note: It is recommended that you change the AP name to a "friendly name" that will help to identify the device. Example: For a repeater Access Point, call it "repeater" or for an Access Point in your conference room, "conference room AP."
Note: It is recommended that you change the SSID from the default. The SSID is case-sensitive.
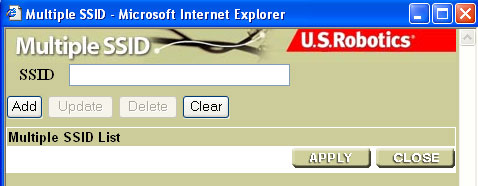
If you want to use the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point to connect to several different networks, you can create an SSID list and enter an SSID for each network. Click Multiple SSID and a new window will open. Enter the SSID you want to use for a specific network and then click Add. Repeat this procedure for each network you want to connect to. Each SSID that you enter will appear in the list. Click Update to modify an entry or Delete to remove it from the list.
For AP mode, you can choose from the following:
- Access Point mode
- AP Client mode
- Wireless Bridge mode
- Multiple Bridge mode
- Repeater mode
Access Point mode
Access Point mode is used to connect up to 20 wireless clients. If you have up to 20 computers, each equipped with a wireless adapter, you can use Access Point mode to create a wireless network among the computers. This is the simplest configuration mode for the Wireless Access Point.
Note: 100Mbps Accelerator Technology is only available in Access Point mode.

AP Client mode
AP Client mode is used to connect any computers that don't support wireless adapters. By connecting a Wireless Access Point to each of these computer via Ethernet, the Wireless Access Point can be used as a wireless adapter.
Note: If your Ethernet device or network adapter does not support auto-switching, you may need to use an Ethernet crossover cable to connect the Wireless Access Point in AP Client mode. Refer to the documentation for your Ethernet device or network adapter to see if it supports auto-switching. The USRobotics Wireless Turbo Multi-Function Access Point supports auto-switching.
Note: If you select AP Client mode, you will need to enter a MAC Address for the Access Point.
- Select Basic Setting on the HTML page.
- Click to select AP Client.
- Enter the LAN Hardware Address of the Router or Access Point to which
you wish to connect. Click Apply at the bottom of the screen.

Wireless Bridge mode
Wireless Bridge mode is used to wirelessly connect two existing wired Local Area Networks (LANs). By connecting a Wireless Access Point to each LAN and selecting Wireless Bridge mode, the two Wireless Access Points will talk only with each other, creating a direct connection between the different networks.
Note: If you select Wireless Bridge mode, you will need to enter a MAC Address for the Wireless Bridge.
- You will be bridging two Access Points together; we will refer to them as Access Point 1 and Access Point 2.
- On Access Point 1, select Basic Setting on the HTML page.
- Click to select Wireless Bridge.
- Enter the LAN Hardware Address of Access Point 2.
- Click Apply at the bottom of the screen.
- On Access Point 2, select Basic Setting on the HTML page.
- Click to select Wireless Bridge.
- Enter the LAN Hardware Address of Access Point 1.
- Click Apply at the bottom of the screen.

Multiple Bridge mode
Multiple Bridge mode is similar to Wireless Bridge mode, but is used when you want to wirelessly connect more than two wired LANs. By connecting a Wireless Access Point to each LAN and selecting Multiple Bridge mode, the multiple Wireless Access Points will talk only with each other, creating a direct connection among the different networks.
- Make sure all Access Points to be bridged are set up identically: same channel, same SSID, same modulation, and same encryption.
- Select Basic Setting on the HTML page.
- Click to select Multiple Bridge.
- Click Apply at the bottom of the screen.
- After the individual Access Points reboot, connect them to appropriate switches or computers depending on your implementation.

Repeater mode
If you have a wireless client that is positioned in your home or office and the transmission signals are weakened, you can use a 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point to boost the signal to and from the wireless clients. By placing the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point between the two clients and selecting Repeater mode, the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point will then fill in the gap in the transmission capabilities and pass any network information between the wireless clients.
To use a 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point in Repeater mode, you must first configure the Access Point using an Ethernet connection. Connect the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point to a computer using an Ethernet cable. Launch the Configuration Utility or the Web Configurator. Select Repeater as the AP Mode, enter any configuration information you may need, and save your changes.
After the Access Point has been configured for Repeater mode, remove the Ethernet connection, position the Access Point in the proper location, and plug in the power supply.
Note: Do not have any Ethernet cables connected after you have configured the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point and are using it in Repeater mode.
- Select Basic Setting on the HTML page.
- Click to select Repeater.
- Enter the LAN Hardware Address of the Router or Access Point from which you wish to repeat.
- Click Apply at the bottom of the screen.
- If you wish to set up additional USR5450 Access Points as repeaters, follow the above instructions for each one, replacing the LAN MAC address for the device from which you wish to repeat.
Note: When 802.1X is enabled on your Access Point, you should select a maximum of 128 bit WEP encryption. Windows clients that have 802.1X enabled may not be able to take advantage of the 256 bit WEP encryption.
IP Setting
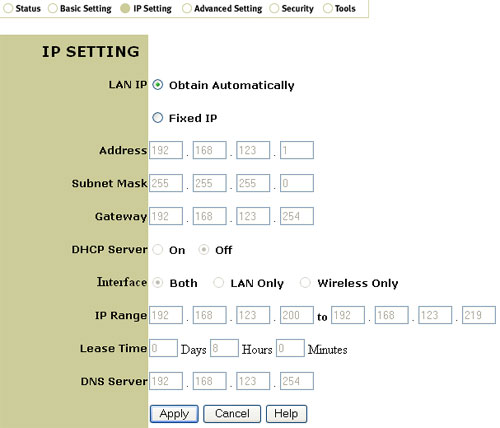
In the IP Setting section you can select either Obtain Automatically or Fixed IP for the LAN IP. If you select Fixed IP, you will need to enter the Address, the Subnet Mask, and the Gateway. You can turn on or off the DHCP Server in this area. If you turn DHCP Server on, you will need to select Both, LAN Only, or Wireless Only for the Interface. This will set whether or not the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point will supply an IP address to wired clients, wireless clients, or both. You will also need to enter an IP Range, Lease Time, and a DNS Server.
Note: Changing the IP Address will require you to manually reconnect to the device after a reboot.
Note: Enabling a DHCP Server should be done as needed only. Multiple DHCP Servers on a network that have not been configured by an administrator can cause a failure in network connectivity.
Note: If you are not connected to an adapter or device that is giving out DHCP addresses, the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point will not obtain an IP Address. Without an IP Address, the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point will still pass wireless network traffic between clients, but you will not be able to configure any of the settings.
Advanced Setting
Only advanced users should change any of the configuration settings in this section.
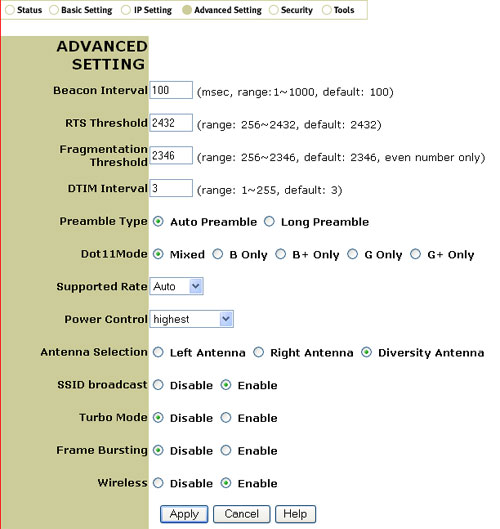
The information for Beacon Interval, RTS Threshold, Fragmentation Threshold, and DTIM Interval is supplied and is configured for optimal performance. Only advanced users should change any of this information.
In Preamble Type, you can select Short Preamble or Long Preamble. If you are in an area where there is a lot of network traffic, Long Preamble should be selected. If you are in an area where there is not a lot of network traffic and you want faster performance, Short Preamble should be selected.
For Dot11Mode, you can select Mixed, B Only, B+ Only, G Only, or G+ Only. If you select Mixed, different types of 802.11 wireless devices will be able to connect to the Wireless Turbo Access Point & Router. If you select one of the other options, only wireless devices of that specific 802.11 type will be able to connect to the Wireless Turbo Access Point & Router. By default, Mixed is selected.
Note: If you select B+ Only or G+ Only, RTS Threshold and Fragmentation Threshold will not be available options.
For Supported Rate, you can select Auto, 1, 2, 5.5, 6, 9, 11, 12, 18, 22, 24, 36, 48, 54, 54/100, or 54/125.
For Power Control, you can select either low, medium low, medium, medium high, or highest. This will determine the signal strength of the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point. If you are in an area that has several wireless access points and do not want to overlap signals or if you are in an area where your wireless signal could easily be detected by unwanted wireless clients, select a lower Power Control setting. If you are in area where you need a stronger signal to be available to all the desired wireless clients or if unwanted wireless clients is not a concern, select a higher Power Control setting.
In Antenna Selection, you can select Left Antenna, Right Antenna, or Diversity Antenna. This will turn on either the left antenna, the right antenna, or both accordingly.
In SSID Broadcast, you can select either Enable or Disable. It is recommended that you select Disable to increase the security of your network and that you change the SSID from the default. The SSID is case-sensitive.
Note: If you disable SSID Broadcast, the correct information must be manually entered for each wireless client that needs to be connected to your wireless network. With SSID Broadcast disabled, wireless clients will not be able to scan and connect automatically to your wireless network.
For Turbo Mode, you can select either Enable or Disable. If you select Enable, all the wireless clients that will be connecting to the wireless network must be 802.11g products in order to utilise the Turbo Mode feature. This will raise the maximum speed from 54 mbps to 100 mbps. If you disable Turbo mode, the Frame Bursting option will not be available.

For Frame Bursting, you can select either Enable or Disable. If you select Enable, all the wireless clients that will be connecting to the wireless network must be 802.11g products in order to utilise the Frame Bursting feature. This will raise the maximum speed from 100 mbps to 125 mbps.
For Wireless, you can select either Enable or Disable. If you select Disable, the wireless funcitionality of the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point will be turned off.
Security
Within the Security section, you can change the security information for the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point.
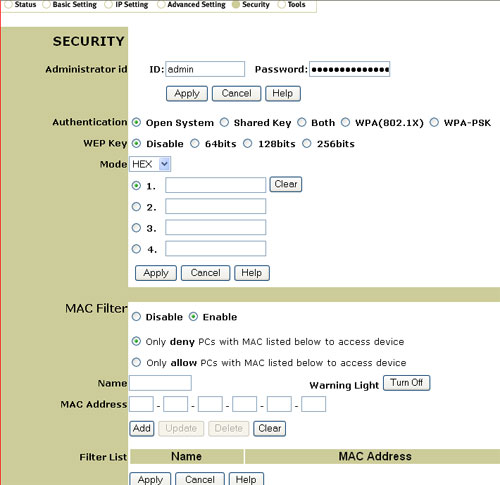
On this page, you can enter an Administrator ID and a Password. If you create these, you must click Apply for the settings to take effect.
You can choose from one of the following options for security type: Open System, Shared Key, Both, WPA (802.1X), or WPA-PSK.
WEP is an encryption scheme that is used to protect your wireless data communications. WEP uses a combination of 64-bit keys, 128-bit keys, or 256-bit keys to provide access control to your network and encryption security for every data transmission. To decode a data transmission, each wireless client on the network must use an identical 64-bit, 128-bit, or 256-bit key.
WPA’s use of keys is very similar to WEP, but the key is only used once to start the process. Once communication is established, the key will randomly change. This provides a higher level of security. It is recommended that you use the most secure mechanism available on your 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point.
Note: WPA and WPA-PSK can only be used if the wireless network you want to connect to is capable of employing WPA or WPA-PSK as an authentication mode. Many older wireless devices may not be able to use WPA or WPA-PSK, so this should be verified before WPA or WPA-PSK is selected. Non-matching authentication modes will keep you from being able to connect to a wireless network.
- Open System, Shared System, or Both
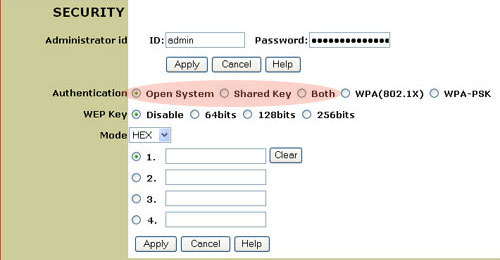
If you enable Open System (WEP), Shared System (WEP), or Both, you will need to select the length of the WEP Key from Disable, 64-bit, 128-bit, or 256-bit. The WEP Key options provide the different levels of security for your network, 64-bit being the lowest and 256-bit being the highest.
You will then need to select the Manual Key Mode of either HEX or ASCII. HEX values are defined as A-F and 0-9 while ASCII uses all characters.
If you enable WEP, you are allowed to store up to four Keys. You must select at least one. The following table details the necessary length of characters that must be input for each WEP key that is activated.
HEXASCII64-bit 10 characters5 characters128-bit 26 characters13 characters256-bit 58 characters29 charactersNote: If 256-bit key encryption is selected, each wireless card or adapter must support 256-bit encryption. If you are using a wireless card or adapter that does not support 256-bit encryption, you will not be able to connect to the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point.
- WPA (802.1X)
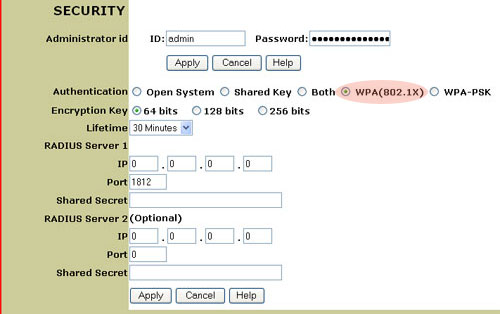
If you enable WPA (802.1X), you will need to select you will need to select the length of the WEP Key from 64-bit, 128-bit, or 256-bit. The WEP Key options provide the different levels of security for your network, 64-bit being the lowest and 256-bit being the highest. This will determine the level of encryption between the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point and the Radius Server. This does not set the level of encryption for the WLAN.
You will then need to select the Lifetime of the encryption. You can choose 5 Minutes, 15 Minutes, 30 Minutes, 1 Hour, 8 Hours, or 1 Day. This will determine how long the encryption will remain in effect.
You will then need to provide the information for RADIUS Server 1. This is the computer to which the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point creates a secure connection. You will need to supply the IP Address of the Radius Server. You also need to supply a Port number for the Radius Server or use the default 1812. You will then need to provide the IP Address of the computer to which you are connecting. Next, you will need to provide the Shared Secret. This can be a word or a set of numbers and will be used as an additional form of security. Each 802.1X wireless client that will connect to the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point must have the correct Shared Secret or the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point will be denied.
The use of RADIUS Server 2 is optional. These fields are used to enter the information for a backup server. If the server computer identified in RADIUS Server 1 is not working or does not respond, RADIUS Server 2 can be used so that you still have WLAN access.
- WPA-PSK
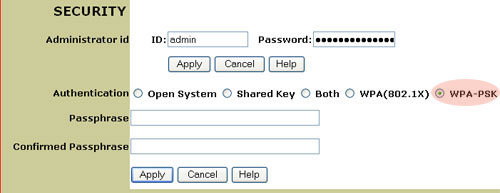
If you enable WPA-PSK, you will need to enter a Passphrase and then enter it again to confirm it. This passphrase must be the same on each computer that is connected to the wireless network.
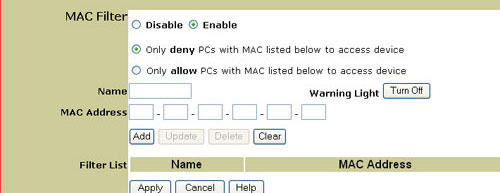
You can select either Enable or Disable for the MAC filter. If you enable the MAC filter, you can enter a name and the MAC addresses of computers that you do not want to connect with the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point wirelessly. After entering this information, click Add and an entry will be added to the Filter List. If you ever need to modify an entry in the list, select the entry and then click Update or Delete. In this area, you can also turn off or on the warning light of the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point.
If you make any changes to the wireless settings, you must click Apply in order for the changes to take effect. If you make any mistakes while applying changes to the settings, click Clear to remove the settings.
Tools
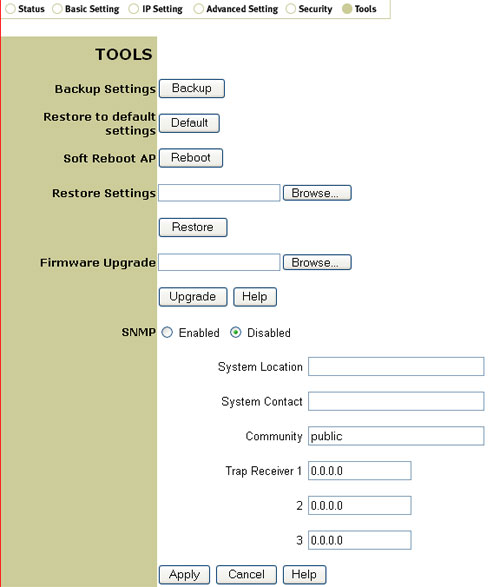
Within the Tools section, you can save the settings of your 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point by clicking Backup.
If you want to restore the default settings of the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point, click Default.
If the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point stops responding, click Reboot and the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point will restart.
If you change your settings and want to retrieve your saved settings, you can click Browse to locate the saved file. Once you locate the saved file, click Restore.
If a new firmware version is made available and you have downloaded it, click Browse next to Firmware Upgrade to locate the correct version file. When you have located it, click Upgrade to implement the new firmware.
SNMP
802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point Telnet Configuration
Another option for configuring the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point is to use Telnet Configuration.
You can access the Telnet Configuration screen from a command prompt window. Click Windows Start and then click Run. In the Run dialog box, Windows 95, 98, and Me users should type command and click OK. Windows NT, 2000, and XP users should type cmd and click OK.
When the command prompt window opens, type Telnet and the IP address of the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point and then press ENTER. When you are prompted for a password, type in the Access Point's password and then press ENTER. This will open up the Telnet Configuration menu.
On each line within each menu there are either configurable parameters with the parameter's current value in parentheses or submenu items. All items have a description next to them describing what the function does. For example, "state" is a submenu item and "passwd" is a configurable parameter. Typing the name of the submenu will take you to the submenu. Typing a configurable parameter will take an argument and set the value to that argument.
When you have completed updating your configuration, you must type save and press ENTER in order for the settings to take effect. Typing save will also cause the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point to reboot. If you make any changes then decide you do not want to save them, type exit to disconnect from the Telnet Configuration. In each option, you can also type back to return to the previous screen or main to return to the main menu screen.
Note: When the device reboots, the Telnet session will be disconnected. You will then need to manually reconnect to the device.

Within this menu there are five options: state, setup, passwd, default, and exit. In every menu, next to the options are the current values of configurations and definitions of what the option is and, if applicable, what your choices are for settings.
State

At the command prompt, type state and press ENTER to view this section. In this section you can see the current connection information for your 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point.
Setup

At the command prompt, type setup and press ENTER to view this section. In this section, there are eight options: lansetup, wireless, advance, security, 802.1x, snmp, back, and main.
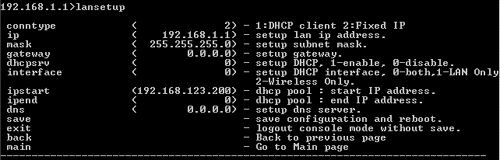
Lansetup
At the command prompt, type lansetup and press ENTER to view the LAN network options. Your options are conntype, ip, mask, gateway, dhcpsrv, and interface.
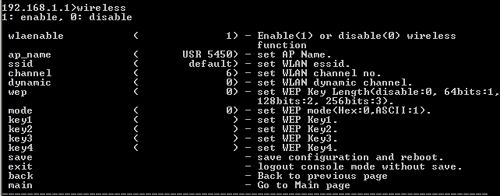
Wireless
At the command prompt, type wireless and press ENTER to view the wireless network options. These options include wlaenable, ap_name, ssid, channel, dynamic, and wep.
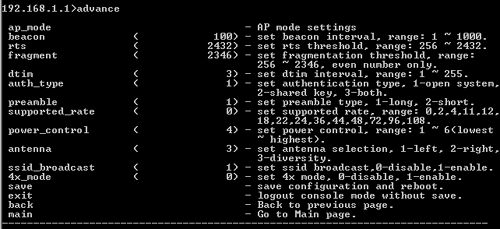
Advance
At the command prompt, type advance and press ENTER to view the advanced network options. These options include ap_mode, beacon, rts, fragment, dtin, auth_type, preamble, supported_rate, power_control, antenna, ssid_broadcast, and 4x_mode.
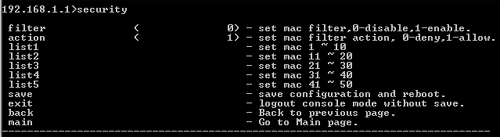
Security
At the command prompt, type security and press ENTER to view the security options of the network. These options include filter, action, list1, list2, list3, list4, and list5.
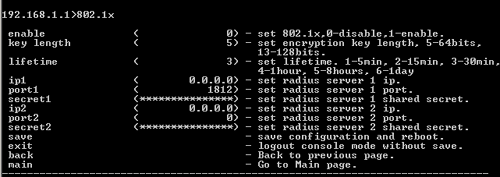
802.1x
At the command prompt, type 802.1x and press ENTER to view the 802.1X options of the network. These options include enable, key length, lifetime, ip1, port1, secret1, ip2, port2, and secret2.
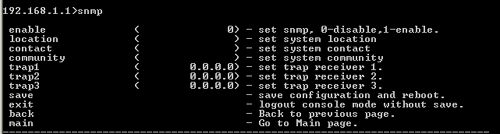
SNMP
At the command prompt, type snmp and press ENTER to view the snmp options of the network. These options include enable, location, contact, community, trap1, trap2, and trap3.
Passwd

At the command prompt, type passwd, type your new password, and then press ENTER to change the password for your 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point.
Default

At the command prompt, type default and then press ENTER to restore the factory default settings of the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point. After the factory default settings are restored, the 802.11g Wireless Turbo Multi-function Access Point will reboot.