The firewall built into the router protects your network from outside attacks, and controls access to the Internet from your network. In the configuration pages, select Firewall. In this section you can configure and change the Firewall settings for the router.
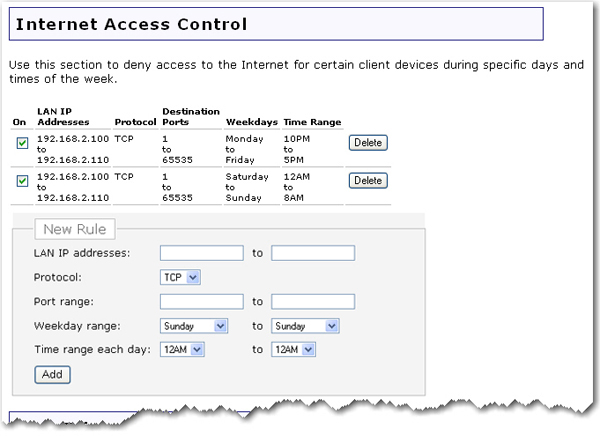
With this option, you can deny Internet access to specific clients during specific days and times of the week. This can be useful if you have children in your home and you want to regulate their Internet usage or if you have multiple people in your small business using the same computer over different shifts and you don't want specific employees to be able to access the Internet.
The router comes with two default access control rules to restrict Internet access to computers with IP addresses between the range of 192.168.2.100 and 192.168.2.110. To enable a rule, select the On checkbox for the rule.
Restrict all Internet access between 10PM and 5PM from Monday to Friday.
Restrict all Internet access between 12AM and 8AM for the weekend, Saturday and Sunday.
For detailed steps on configuring your own Internet Access Control rules, see the Parental Controls section on the Tutorials page.

To add entries for this feature, you will need to complete the following steps:
Specify the range of LAN IP addresses or a single IP address.
Specify the Protocol, either TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) or UDP (User Datagram Protocol).
Specify the Port range or enter a single specific port to block.
Specify the Weekday range and the Time range each day.
When you have specified these settings, click Add.
Repeat steps 1 through 4 for any additional entries.
Click Save at the bottom of the page when you are finished.
Some applications connect to the Internet by using one or more outbound ports expecting the remote host to connect back at one or more inbound ports. The router, by default, blocks all incoming connections. Port Triggering configures the router's firewall to allow the incoming connections to reach the client devices.
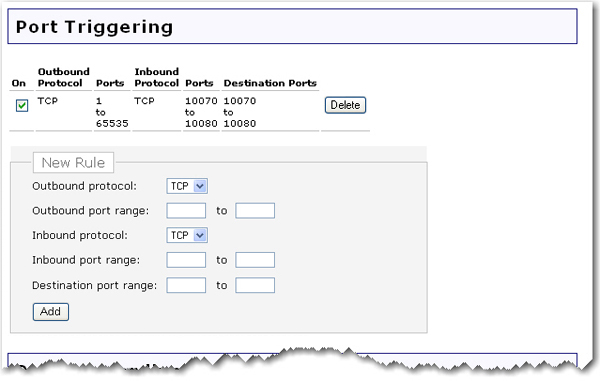
The router comes with a default Port Triggering rule that you will need if you are connecting a Sony Playstation2™ that needs to access the Internet to your router. To enable the rule, select the On checkbox for the rule.
For detailed steps on configuring your own Port Triggering rules, including Port Triggering details for a Microsoft Xbox®, see the Tutorials page.
Note: Opening ports on a router can cause potential security risks. In particular, opening Terminal Services UPnP Port 3389 on Windows XP can allow Internet hackers to take over your computer if Windows XP is not patched with Microsoft's latest security updates.
For a complete list of applications and port information, visit www.iana.org
To add entries for this feature, complete the following steps:
Specify the Outbound protocol (TCP/UDP).
Specify the Outbound port range of the destination ports for outbound traffic which will cause this Port Trigger to activate.
Specify the Inbound protocol (TCP/UDP).
Specify the Inbound port range of the destination ports for inbound traffic. The router will allow inbound traffic on these ports when the Port Trigger is active.
Specify the Destination port range for the ports the inbound connection will be translated to. When this Port Trigger is active, the router will translate the destination port of an inbound connection to this port range.
When you have specified these settings, click Add.
Repeat steps 1 through 5 for any additional entries.
Click Save at the bottom of the page when you are finished.
With Port Forwarding, you can direct inbound traffic to specific clients on your network. Ports are connections that are used by a computer to organize the various forms of network traffic. A port can support both ingoing and outgoing network traffic, or just one-way network traffic.
If you open a port, a specific service will be assigned to it and that service will communicate with the network only through that port. Some applications require open service ports, such as Internet games, video conferencing, Internet telephony, and others.
An example of when you might want to enable this feature is if you are running a Web server on one of your network clients. By enabling Port Forwarding, traffic to that Web site would pass through the router and go directly to the appropriate network client, instead of going through the router and suddenly having access to your whole network.
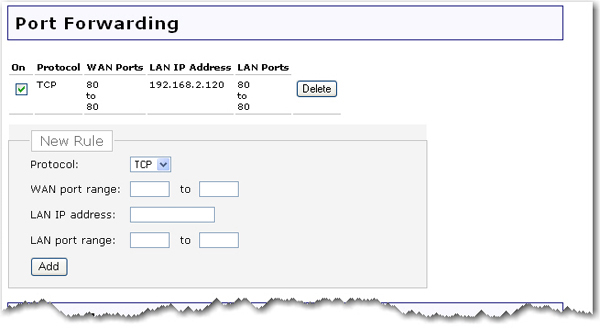
As an example, the router comes with a default port forwarding rule for a Web server on your network where the ports for Web traffic (80) need to direct to the IP address for the Web sever (default IP address: 192.168.2.120). To enable the rule, select the On checkbox for the rule.
For detailed steps on configuring your own Port Forwarding rules, see the Tutorials page.
Note: Opening ports on a router can cause potential security risks. In particular, opening Terminal Services UPnP Port 3389 on Windows XP can allow Internet hackers to take over your computer if Windows XP is not patched with Microsoft's latest security updates.
To add entries for this feature, complete the following steps:
Specify the Protocol and the WAN port range. The router will allow incoming traffic on these incoming ports of the previously mentioned protocol type to pass through the firewall.
Specify the LAN IP address and the LAN port range of ports the incoming traffic will be forwarded to.
When you have specified these settings, click Add.
Repeat steps 1 through 3 for any additional entries.
Click Save at the bottom of the page when you are finished.
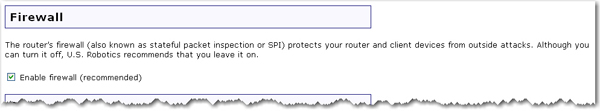
If you deselect the checkbox next to Enable firewall, the firewall will be disabled, but this is not recommended. The firewall is used to block unauthorised users from accessing the network or any of the network resources. A firewall is one of the most critical pieces of security you can use in your network.
The DMZ (Demilitarised Zone) is a computer that has all external Internet traffic forwarded to it, such as a public Web server. This allows a computer to be exposed to unrestricted two-way communication. This feature should be used with caution, since it removes the security of the firewall for that computer.

If you want to specify a DMZ, enter the client computer's IP address. When you are finished, click Save.
Note: You need to click Save to save all your new settings and reboot the router after you have completed all your changes.