Forwarding Rules
 |
The Forwarding Rules menu gives you the following options:
- Virtual Server gives access to the router's services, such as the Internet, FTP, and email, to other users on your network.
- Special Application Port lets applications, such as Internet games, that normally would be blocked at the firewall communicate with network devices.
- Miscellaneous lets you set up the use of a DMZ and an FTP server.
|
Virtual Server
The Broadband Router with USB Print Server's NAT firewall filters out unrecognised packets to protect your local network.
All computers behind the firewall are invisible externally.
You can make some of them accessible by enabling them in the Virtual Server's map.
The Virtual Server function is also known as port forwarding.
Virtual Server sets up public services on your network.
When an external Internet user makes a request to a specific port in your network,
the router will forward that request to the appropriate computer.
The computer must be configured with a static IP address in order to be recognised by the Virtual Server.
A virtual server is defined as an IP address and a service port, and all requests to this port will be redirected
to the computer associated with this port in the Virtual Server.
For example, if you have an FTP server (port 21) at 192.168.123.1, a Web server (port 80) at 192.168.123.2,
and a VPN server (port 1723) at 192.168.123.6, then you need to specify the following virtual server mapping table:
| Service Port |
Server IP |
Enable |
| 21 |
192.168.123.1 |
√ |
| 80 |
192.168.123.2 |
√ |
| 1723 |
192.168.123.6 |
√ |
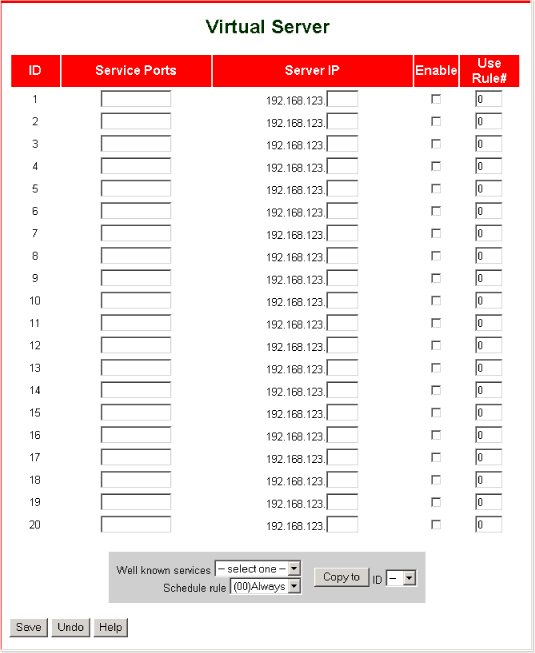
To add a service using Virtual Server, perform the following steps:
- Enter the Service Ports number.
OR
Select an item from Well known services, select a unique ID number, and click Copy to.
- Enter the Server IP address of the machine
to which you want to allow access from the Internet.
- Check Enable.
Follow steps 1–3 above for additional services as needed.
- Click Save in order to save the settings.
Virtual Server can work with schedule rules, giving you more flexibility in access control.
To associate a schedule rule with a virtual server ID line:
- Select a rule from the Schedule rule list.
- Select the line ID from the ID list.
- Click Copy to.
- Click Save in order to save the settings.
For more information about schedule rules, see Schedule Rule under Security Settings in this guide.
Special Application Port
Some applications, such as Internet games, video conferencing, and Internet telephony,
require that outside parties, or parties on the WAN side, have access to open ports.
Because your router's firewall protects your system by closing ports when not in use,
the outside parties do not have access to machines on the routerís LAN side (your Local Area Network).
The Special Application Port option lets you grant access to an outside party when an application
on the LAN initiates a connection to the outside party.
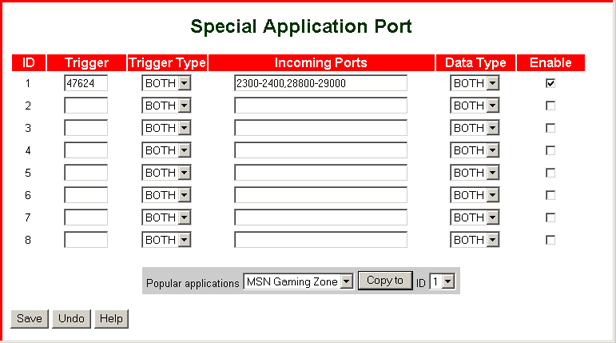
To establish an open service port for external applications, perform the following steps:
- Under Trigger, enter the outbound port number used by the application.
OR
Select an item from the Popular applications list box, select a unique ID number, and click Copy to.
- Under Trigger Type, select the protocol that the special application uses for the trigger on the LAN side.
- Under Incoming Ports, specify the port number to be allowed through the firewall when the trigger packet is detected. If you use the Copy to option to select a trigger, the incoming port is automatically filled in for you. If you specify the incoming port manually, you can specify a single port, multiple ports, a range of ports, or multiple ranges of ports.
To specify multiples, use a comma as a separator. To specify a range, use a hyphen between the first and last port number in the range. These rules are illustrated in the following table:
| |
Incoming Ports specification |
| single port |
10000 |
| multiple ports |
10000,10001 |
| range of ports |
10000-11000 |
| multiple ranges of ports |
10000-11000,13000-15000 |
- Under Data Type, select the protocol that the special application uses for inbound packets on the WAN side.
- Check Enable.
- Set up as many service ports as you need.
- Click Save.
Note: Only one computer can use a given special application port at a time.
If you establish a special application port but the application still does not function correctly,
consider specifying a DMZ host.
Miscellaneous
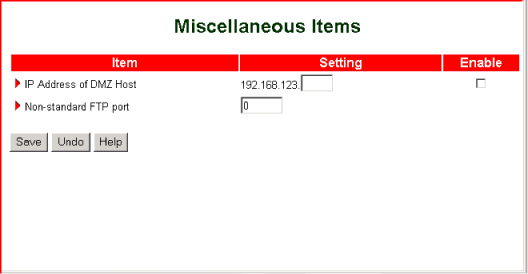
IP Address of DMZ Host
A DMZ (Demilitarised Zone) host is a computer without the protection of the firewall.
The DMZ feature allows a computer to be exposed to unrestricted two-way communications for Internet games,
video conferencing, Internet telephony and other special applications. Use this feature only when necessary.
Non-standard FTP Port
Use this option to enable access to an FTP server whose port number is not 21.



