
Contents:
Dialing, Answering, and Hanging Up
Controlling Result Code Displays
Accessing and Configuring the Courier 56K Corporate Modem Remotely
Handshaking, Error Control, Data Compression, and Throughput
Displaying Querying and Help Screens
Dedicated/Lease Line and Synchronous Applications
Appendixes
Technical Information
Courier 56K Corporate Modem Command Reference
Technical Information
Your modem uses multiple standard data communications protocols and is also compatible with many nonstandard schemes. The following schemes are supported:
- Modulation
- Error Control, Data Compression, Testing, and Dialing
- New Connect Messages
- Specifications
- Serial Ports
- The EIA-232 Interface
- Wiring a DB-25 to DB-9 Cable
- Minimum Requirements
- Flow Control Requirements
Modulation
|
This modulation
|
Supports
|
| V.90 | ITU 56K standard, server capabilities. |
| ITU-T V.34 | 33.6/31.2/28.8/26.4/24/21.6/19.2/16.8/14.4/12 kbps; 9600/7200/4800 bps asynchronous Trellis Coded Modulation (TCM) |
| V.FC | 28.8/26.4/24/21.6/19.2/16.8/14.4 kbps asynchronous TCM |
| V.32 terbo | 21.6/19.2/16.8/14.4/12 kbps; 9600/7200 bps asynchronous TCM; 4800 bps asynchronous Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) |
| HST | 16.8/14.4/12 kbps; 9600/7200 bps asynchronous, asymmetrical, 450 bps back channel with automatic handshake adjustment to 300 bps TCM and QAM; 4800 bps asynchronous, asymmetrical, 450 bps back channel with automatic handshake adjustment to 300 bps QAM. |
| ITU-T V.32 bis | 14.4/12 kbps; 9600/7200 bps asynchronous TCM; 4800 bps asynchronous QAM |
| ITU-T V.32 | 9600 bps asynchronous, TCM; 4800 bps asynchronous, QAM |
| ITU-T V.22 bis | 2400 bps asynchronous, QAM |
| Bell 212A | 1200 bps (also V.22) asynchronous, Differential Phase Shift Keying (DPSK) |
| ITU-T V.23 | 1200 bps asymmetrical with 75 bps back channel with Frequency Shift Keying (FSK), used by some U.K. and European phone systems. |
| Bell 103 | 300 bps (ITU-T V.21 optional) asynchronous, Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) |
Error Control, Data Compression, Testing, and Dialing
|
This modulation
|
Supports
|
| ITU-T V.42 | LAPM error control, 1200 bps and higher |
| MNP | Levels 2, 3 and 4 error control, level 5 data compression, 1200 bps and higher |
| HST | Asymmetrical mode, at 16.8/14.4/12 kbps; 9600/ 7200/4800 bps, 450/300 bps back channel |
| ITU-T V.42 bis | Data compression, 1200 bps and higher |
| ITU-T V.54 | Digital and remote digital loopback testing |
| ITU-T V.25 bis | Dialing and answering method for automatic calling and/or answering equipment |
Fax
Your Courier 56K Corporate modem provides Group III -compatibility when controlled by Class 1 or Class 2.0 fax software. In addition, your Courier 56K Corporate modem adheres to the following standards:
|
This modulation
|
Supports
|
| TIA/EIA-578 | Service Class 1 Asynchronous Facsimile DCE Control Standard |
TIA/EIA-592 |
Service Class 2.0 Asynchronous Facsimile DCE Control Standard |
| ITU-T V.17 | 14.4/12 kbps |
| ITU-T V.29 | 9600/7200 bps |
| ITU-T V.27 | ter 4800/2400 bps |
| ITU-T V.21 | 300 bps |
Specifications
|
This feature
|
Supports
|
||
Supported serial port rates |
230400, 115200, 57600, 38400, 19200, 9600, 4800, 2400, 1200, and 300 bps | ||
| Adaptive Speed Leveling (ASL) | 21600, 19200, 16800, 14400, 12000, 9600, 7200, and 4800 bps | ||
| Serial port connector | DB-25 | ||
Communications channel |
Full- or half- duplex on 2-wire phone lines; demand-driven high-speed turnaround in HST mode; symmestrical speeds in V.32 bis. | ||
| Data format | Binary, serial; defaults to 8-bit word length, no parity, and 1 stop bit. | ||
|
Word Length
|
Parity (1 Bit)
|
Stop Bits
|
|
|
7
|
Even, odd, mark, space
|
1
|
|
|
7
|
None
|
2
|
|
|
8
|
None
|
1
|
|
| Flow Control Buffers | Variable sizes | ||
| Command Buffer | 56 characters, excluding the AT prefix, Carriage Return, and spaces | ||
| Test Options | Remote digital loopback, digital loopback, test pattern, and dial test | ||
| Failed Call Timeout | 60 second default, programmable 2-255 sec. | ||
| Answer Tone Timeout | 60 seconds | ||
| Answer Tone Detector | 2080-2120 Hz | ||
| Loss of Carrier (Disconnect Timer) | 0.7 second default, programmable 0.2-25.5 sec. | ||
| Equalization | Adaptive | ||
| Receive Sensitivity | - 43 dBm + 2 dBm | ||
| Transmit Level | - 9 dBm maximum | ||
| Transmitter Frequency Tolerance | .01% | ||
| Certification | FCC 15, EN55022 (CISPR 22), ICES-003, AS/NZS3548, VCCI; Class B; EN50082-1; UL/C-UL, IEC 950, EN60950, TS001; FCC 68, CTR 21 | ||
Ringer equivalence |
0.4b | ||
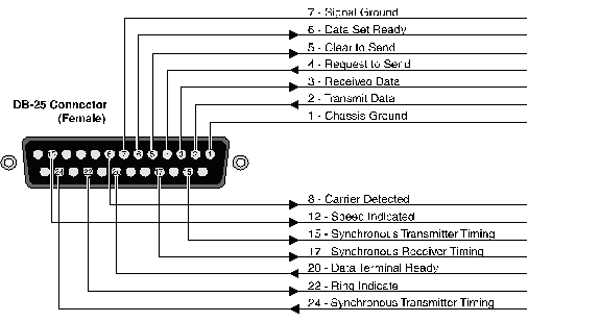
Serial Ports
Most computers provide a DB-25 or DB-9 port that conforms to the EIA-232 standard.
The EIA-232 Interface
Your modem’s serial port is factory set to signal according to the EIA-232 standard.
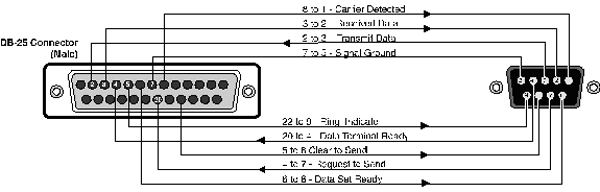
Wiring a DB-25 to DB-9 Cable
DB-9 connectors for PCs should be wired at the computer end of the cable
as shown below.
Minimum Requirements
Some computer/terminal equipment supports only a few of your modem’s EIA-232 signals. The minimum required for your modem to operate asynchronously follows:
| DB-25 | DB-9 | Supports this signal |
| Pin | Pin | Function |
| 2 | 3 | Transmitted Data |
| 3 | 2 | Received Data |
| 7 | 5 | Signal Ground |
| 20 | 4 | Data Terminal Ready |
Flow Control Requirements
If your computer and software support Clear to Send and you wish to use Transmit Data hardware flow control (&H1), Pin 5 (DB-25) or Pin 8 (DB-9) is required.
If your computer and software support Request to Send and you wish to use Received Data hardware flow control (&R2), Pin 4 (DB-25) or Pin 7 (DB-9) is required.