
Contents:
About the 802.11g Wireless Gaming Adapter and Ethernet Bridge
Accessing the Web User Interface and Site Survey
Web User Interface and Security Configuration
802.11g Wireless Gaming Adapter and Ethernet Bridge User Guide
Status Page
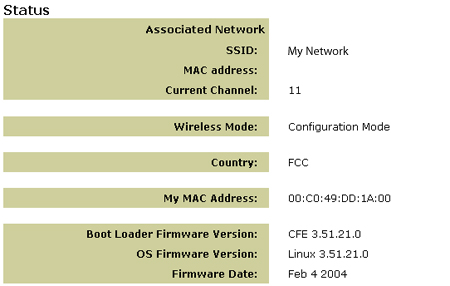
The Status page displays the particular status of, amongst other informative
details, the network you’re associated to, including the SSID name, what
channel you’re broadcasting on, and what firmware version your are using.
Note: If the MAC address field displays a “Device not associated” message, this indicates your 5430 is not associated to your wireless network. If, however, the MAC address field displays a valid MAC address, this indicates that your 5430 is associated to your wireless network.
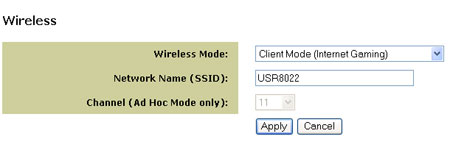
Wireless Menu Options
Use the Wireless menu to change your mode from Client to Ad Hoc Mode and enter a Network Name (SSID) or select a unique channel for Ad Hoc Mode. If you are not sure of the SSID of your network, use the Site Survey feature under Tools to locate a network near the 5430.
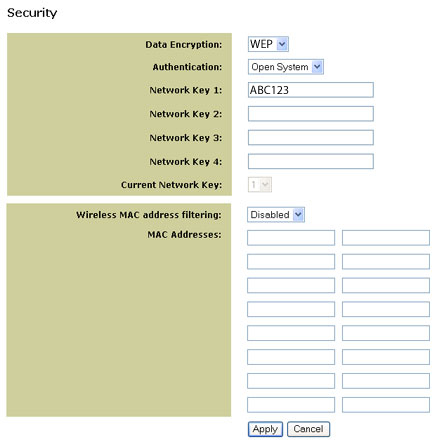
Security: Using a secure wireless network
A wireless network offers you the freedom to roam without the burden of cables but it also means that your data is accessible to anyone else in range of your wireless grid. If you are concerned about a neighbor or someone within range of your wireless network using your wireless connection for malicious activity, we strongly recommend that you enable wireless security to prevent unauthorized connection or someone from eavesdropping to listen in on your network traffic. Today, many wireless routers provide several mechanisms for securing a wireless network and it is recommended that you first enable security on your wireless router and then match the method you have selected on your clients.
USRobotics recommends any one or both of the following two methods:
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
Your 5430 supports 64-bit and 128-bit WEP security. If available on
your wireless router, we recommend you enable the higher bit security.
When you enable WEP, it uses a key to encrypt the data and this specifically
formatted data can only be understood by another wireless device that
knows of this key. Since both ends use the same key, any users who do
not know the key cannot connect to your network and use your Internet
connection.
MAC Address filtering
Many wireless routers provide a mechanism for creating a list of devices
that can participate in your wireless network. Refer to your wireless
router or access point’s documentation to learn if MAC Address filtering
is supported.
Enabling security on your 5430
Enabling WEP
After you have obtained your network name (SSID configured on your wireless
router or access point and its security settings), you can use the Security
menu located on the Web User Interface pages to program your 5430 for
WEP security.

If you select WEP, you have the option to enforce Shared Key Authentication (Forced) or let the 5430 send it only when a wireless router requests it (Open System).
It is important that you match the Network Keys with those of your wireless
routers. If you have multiple Network Keys, you can enter up to four keys.
Note: Network Keys are case sensitive. When entering a Network Key, be sure you insert the key exactly as it appears in your wireless router or access point.
Wireless MAC Filtering
You can use MAC Address filtering to connect only to a specific wireless
router or access point. You can add the MAC Address of your wireless router
or access point and change the “Wireless MAC address filtering” field
to Allow. In doing so, your 5430 will only “talk” to your wireless router
or access point and cannot be accessed by other devices.
Advance Menu Options
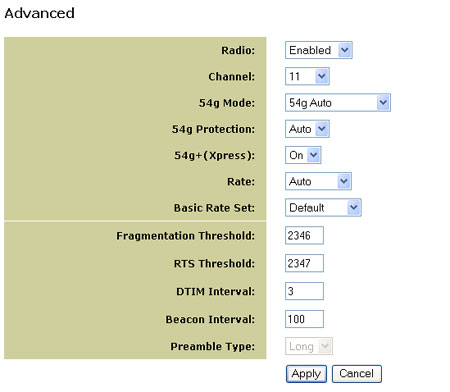
Radio
Use the Radio menu to enable and disable wireless signal transmission.
If you want to shut down the signal of your unit (disconnect from the
wireless network), select Radio Off.
Channel
802.11b and 802.11g use channels to limit interference from other devices.
If you are experiencing interference with another 2.4Ghz device such as
a baby monitor, security alarm, or cordless phone, change the channel
on your 5430 as well as your wireless router. The channel feature will
be used mostly in Ad Hoc Mode. In Client Mode, the 5430 automatically
switches the channel to match the one from the wireless router or access
point.
54g Mode
If you are having difficulty connecting to an 802.11b wireless only router,
try switching your 5430 to 802.11b only mode and do the same with your
wireless router. This will ensure you are connecting to 802.11b devices
only. Set the mode to 54g Auto for the widest compatibility. Set the mode
to 54g Performance for the fastest performance among 54g certified equipment.
54g Protection
The 802.11g standards provide a protection method so 802.11g and 802.11b
devices can co-exist in the same network without “speaking” at the same
time. Do not disable 54g Protection if there is a possibility that a 802.11b
device may need to use your wireless network. In Auto Mode, the wireless
device will use RTS/CTS to improve 802.11g performance in mixed 802.11g/802.11b
networks. Turn protection off to maximize 802.11g throughput under most
conditions.
54g+ (Xpress)
54g+ is a technology that utilizes standards based on framebursting to
achieve higher throughput. With 54g+ enabled, aggregate throughput (the
sum of the individual throughput speeds of each client on the network)
can improve by up to 25% in 802.11g only networks and up to 75% in mixed
networks comprised of 802.11g and 802.11b equipment.
Rate
You may force a lower data rate if you are having trouble getting connected
or losing data at a higher rate. It is important to know that some data
rates belong only to one 802.11 standard but not the other which will
force your 5430 to connect to only that network. 802.11g rates; 6,
9, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, 54 Mbps 802.11b rates: 1, 2, 5.5, 11 Mbps
Basic Rate Set
You have the option of supporting all rates as listed in the Rate section
above or using the 1, 2 Mbps rates which will support only older 802.11b
implementations.
Fragmentation Threshold
This threshold is used to fragment packets which help improve performance
in the presence of RF interference.
RTS Threshold (Request to Send Threshold)
The RTS threshold determines the packet size of a transmission and, through
the use of an access point, helps control traffic flow.
DTIM Interval
The DTIM Interval sets the Wake-up interval for clients in power-saving
mode.
Beacon Interval
A beacon is a packet of information that is sent from a connected device
to all other devices where it announces its availability and readiness.
A beacon interval is a period of time (sent with the beacon) before sending
the beacon again. The beacon interval may be adjusted in milliseconds
(ms).
Preamble Type
Preambles are a sequence of binary bits that help the receivers synchronize
and ready for receipt of a data transmission. Some older wireless systems
like 802.11b implementation use shorter preambles. If you are having difficulty
connecting to an older 802.11b device, try using a short preamble. You
can select short preamble on if the 54g mode is set to 802.11b Only in
the 54g Mode field.
Changing Between Client and Ad Hoc Modes
To change between Client and Ad Hoc Modes, simply access the Web User Interface, select Setup, and follow the on-screen instructions as demonstrated in the graphics below:

Or, you can also switch between modes by selecting the Wireless tab, selecting the appropriate mode from the Wireless Mode field, and selecting Apply.
Upgrading Your Adapter
Download and place the firmware file to a local directory. Place the 5430 in Configuration Mode (insert a pin or paperclip to press the reset button momentarily - less than 2 seconds). Connect the Ethernet cable to your computer’s Ethernet port and release and renew your computer’s IP address (refer to the Accessing the 5430’s Web User Interface pages in this User Guide for more information). Launch an Internet browser and enter http://192.168.1.201 in the address line. Enter the username (the default username is admin) and the password (the default password is admin) to access the Web User Interface. Select the Tools tab. From the New Firmware line, select Browse and locate where the downloaded firmware file was placed. Select Upgrade to start the upgrade. It is important that you do not unplug the cable or interrupt the upgrade. Allow several minutes for the adapter to reboot after the upgrade.
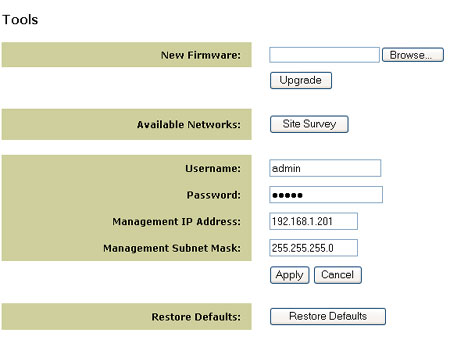
Tools Menu Options
Site Survey will search for all networks (SSID) in range of the adapter and allow you to select one for association. In case the selected network uses encryption, you first need to setup encryption on your 5430 using the Security tab (refer to your wireless router or access point documentation for specific networking security information).
Use the Tools menu to change the 5430 login account, modify the 5430’s management IP address and subnet mask, and restore the 5430 to factory defaults.
