Contents:
Hardware Installation >
Wireless Cable/DSL Router User Guide (Windows 95, 98, 2000, NT, Me, XP, and Macintosh)
Hardware Installation
A. Connecting a Cable modem to the Wireless Cable/DSL Router.
B. Connecting a DSL modem to the Wireless Cable/DSL Router.
C. Connecting an analogue or ISDN modem to the Wireless Cable/DSL Router.
A. Connecting a Cable modem to the Wireless Cable/DSL Router
- Turn off your PC and your Cable modem.
Locate the Ethernet cable from your Cable modem that is connected to your PC’s Ethernet adapter. Disconnect that Ethernet cable from your PC’s Ethernet adapter and connect it to the WAN port on the rear of the Wireless Cable/DSL Router.

Note: If your Cable modem is connected to your PC using a USB cable, disconnect the
USB cable from both your PC and from your Cable modem.
- To make an Ethernet connection: Connect one end of the supplied
Ethernet cable to your PC's Ethernet adapter. Connect the other end
to one of the LAN ports on the Wireless Cable/DSL Router.
To make a Wireless connection: Make sure each Wireless Card that will be connecting is set to Infrastructure mode.
Note: Each Wireless PC Card or PCI Adapter in the wireless network must have Infrastructure mode selected in the Configuration Utility. Refer to your Wireless Access PC Card or PCI Adapter documentation for information on selecting Infrastructure mode.

- Turn on your Cable or DSL modem. Connect the included power cord to
the power jack on the Wireless Cable/DSL Router. Plug the power cord
into a standard power outlet. Turn on your computer.

Congratulations!
The installation procedure is now complete. You should now have secure and shared Internet access. To verify your connection, launch a Web browser and go to www.usr.com. If the page loads, you are finished with the installation procedure.
If you have any difficulties connecting to the Wireless Cable/DSL Router,
check the top three issues below and see if they apply to your situation.
- If you are attempting to create a Wireless connection but cannot connect
to the Wireless Cable/DSL Router, make sure each Wireless Card is set
to Infrastructure mode. If the Wireless Cards are set to 802.11b
AdHoc mode, you will not be able to connect to the Wireless Cable/DSL
Router. When each Wireless Card is set to Infrastructure mode,
it should automatically connect to the Access Point of the Wireless
Cable/DSL Router. When you first set up the Wireless Cable/DSL Router,
it may take a few moments for your Wireless Cards to detect the Access
Point. If they do not automatically connect, rescan until they will
detect it and connect. If you continue to have problems, refer to the
“Troubleshooting” section of this Guide.
- If you create a Wireless connection to the Wireless Cable/DSL Router
but are experiencing poor link quality, check the positioning of the
Wireless Cable/DSL Router. Long distances, multiple floors, steel or
concrete walls, or other wireless devices can diminish the link quality.
If possible, reposition the Wireless Cable/DSL Router to reduce the
effect of any of these obstacles.
- If you have the Wireless Cable/DSL Router properly connected and can access the Internet, but are experiencing difficulties connecting with special applications (i.e. ICQ, Battle.net, etc.), you must assign specific ports. This will allow the special applications to pass through the firewall function of the Wireless Cable/DSL Router. For more information about how to configure this function, refer to the “Special Applications” section within the “Configuring the Wireless Cable/DSL Router” chapter of the User Guide.
If you are still experiencing any difficulties, proceed to the “Troubleshooting” section of this Guide.
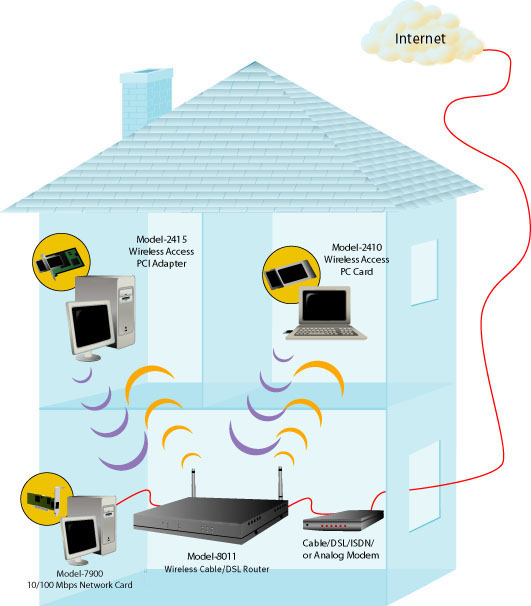
The following graphic is a representation of your system topology after
the installation of the
Wireless Cable/DSL Router.
Connecting a DSL modem to the Wireless Cable/DSL Router
The following graphic is a representation of your system topology before
the installation of the
Wireless Cable/DSL Router.
- Turn off your PC and your DSL modem.
Locate the Ethernet cable from your DSL modem that is connected to your PC’s Ethernet
adapter. Disconnect that Ethernet cable from your PC’s Ethernet adapter and connect it to the WAN port on the rear of the Wireless Cable/DSL Router.

Note: If your Cable or DSL modem is connected to your PC using a USB cable, disconnect
the USB cable from both your PC and from your DSL modem.
- To make an Ethernet connection: Connect one end of the supplied
Ethernet cable to your PC's Ethernet adapter. Connect the other end
to one of the LAN ports on the Wireless Cable/DSL Router.
To make a Wireless connection: Make sure each Wireless Card that will be connecting is set to Infrastructure mode.
Note: Each Wireless PC Card or PCI Adapter in the wireless network must have Infrastructure mode selected in the Configuration Utility. Refer to your Wireless Access PC Card or PCI Adapter documentation for information on selecting Infrastructure mode.

- Turn on your DSL modem. Connect the included power cord to the power
jack on the Wireless Cable/DSL Router. Plug the power cord into a standard
power outlet. Turn on your computer.

Congratulations!
The installation procedure is now complete. You should now have secure and shared Internet access. To verify your connection, launch a Web browser and go to www.usr.com. If the page loads, you are finished with the installation procedure.
If you have any difficulties connecting to the Wireless Cable/DSL Router,
check the top three issues below and see if they apply to your situation.
- If you are attempting to create a Wireless connection but cannot connect
to the Wireless Cable/DSL Router, make sure each Wireless Card is set
to Infrastructure mode. If the Wireless Cards are set to 802.11b
AdHoc mode, you will not be able to connect to the Wireless Cable/DSL
Router. When each Wireless Card is set to Infrastructure mode,
it should automatically connect to the Access Point of the Wireless
Cable/DSL Router. When you first set up the Wireless Cable/DSL Router,
it may take a few moments for your Wireless Cards to detect the Access
Point. If they do not automatically connect, rescan until they will
detect it and connect. If you continue to have problems, refer to the
“Troubleshooting” section of this Guide.
- If you create a Wireless connection to the Wireless Cable/DSL Router
but are experiencing poor link quality, check the positioning of the
Wireless Cable/DSL Router. Long distances, multiple floors, steel or
concrete walls, or other wireless devices can diminish the link quality.
If possible, reposition the Wireless Cable/DSL Router to reduce the
effect of any of these obstacles.
- If you have the Wireless Cable/DSL Router properly connected and can access the Internet, but are experiencing difficulties connecting with special applications (i.e. ICQ, Battle.net, etc.), you must assign specific ports. This will allow the special applications to pass through the firewall function of the Wireless Cable/DSL Router. For more information about how to configure this function, refer to the “Special Applications” section within the “Configuring the Wireless Cable/DSL Router” chapter of the User Guide.
If you are still experiencing any difficulties, proceed to the “Troubleshooting” section of this Guide.
The following graphic is a representation of your system topology after
the installation of the
Wireless Cable/DSL Router.

Connecting an Analogue or ISDN modem to the Wireless Cable/DSL Router
There are two main reasons why you would want to use either an analogue
or ISDN modem
with the Wireless Cable/DSL Router:
You use Dial-up Internet service instead of Cable or DSL Internet service.
You have Cable or DSL Internet service but want to have an analogue or
ISDN backup in case
your broadband Internet service is unavailable.
The following graphic is a representation of your system topology before
the installation of the
Wireless Cable/DSL Router.
Perform the following steps to connect an analogue or ISDN modem, manually
change the WAN
type, and properly configure the Wireless Cable/DSL Router:
- Turn off your PC and your analogue or ISDN modem.
Connect a serial modem cable to your analogue or ISDN modem and to the COM port on the Wireless Cable/DSL Router.

Note: If your analogue or ISDN modem is connected to your PC using a USB cable, disconnect the USB cable from both your PC and from your analogue or ISDN modem.
- To make an Ethernet connection: Connect one end of the supplied
Ethernet cable to your PC's Ethernet adapter. Connect the other end
to one of the LAN ports on the Wireless Cable/DSL Router.
To make a Wireless connection: Make sure each Wireless Card that will be connecting is set to Infrastructure mode.
Note: Each Wireless PC Card or PCI Adapter in the wireless network must have Infrastructure mode selected in the Configuration Utility. Refer to your Wireless Access PC Card or PCI Adapter documentation for information on selecting Infrastructure mode.
- Turn on your analogue or ISDN modem. Connect the included power cord
to the power jack on the Wireless Cable/DSL Router. Plug the power cord
into a standard power outlet. Turn on your computer.

- Launch a Web browser. In the location or address line of your Web
browser, type http://192.168.123.254
to access the Configuration Utility. There is no default password for
the Wireless Cable/DSL Router, so just click Login. Click Primary
Setup and follow the on-screen instructions. When prompted, select
the WAN type as Dial-up Modem and continue to follow the on-screen
instructions. You will need to enter the network information for your
ISP account, such as username, password, and dial-up number.
Congratulations!
The installation procedure is now complete. You should now have secure and shared Internet access. Click Connect to initiate a dial-up session with your ISP. The Status page will indicate whether or not the call was successful. If the settings are correct, the analogue or ISDN modem can be used to connect to the Internet. If the connection fails, verify that you entered the correct values.To verify your connection, launch a Web browser and go to www.usr.com. If the page loads, you are finished with the installation procedure. If the page does not load, proceed to the “Troubleshooting” section of this Guide.
If you have any difficulties connecting to the Wireless Cable/DSL Router, check the top three issues below and see if they apply to your situation.
- If you are attempting to create a Wireless connection but cannot connect
to the Wireless Cable/DSL Router, make sure each Wireless Card is set
to Infrastructure mode. If the Wireless Cards are set to 802.11b
AdHoc mode, you will not be able to connect to the Wireless Cable/DSL
Router. When each Wireless Card is set to Infrastructure mode,
it should automatically connect to the Access Point of the Wireless
Cable/DSL Router. When you first set up the Wireless Cable/DSL Router,
it may take a few moments for your Wireless Cards to detect the Access
Point. If they do not automatically connect, rescan until they will
detect it and connect. If you continue to have problems, refer to the
“Troubleshooting” section of this Guide.
- If you create a Wireless connection to the Wireless Cable/DSL Router
but are experiencing poor link quality, check the positioning of the
Wireless Cable/DSL Router. Long distances, multiple floors, steel or
lead walls, or other wireless devices can diminish the link quality.
If possible, reposition the Wireless Cable/DSL Router to reduce the
effect of any of these obstacles.
- If you have the Wireless Cable/DSL Router properly connected and can access the Internet, but are experiencing difficulties connecting with special applications (i.e. ICQ, Battle.net, etc.), you must assign specific ports. This will allow the special applications to pass through the firewall function of the Wireless Cable/DSL Router. For more information about how to configure this function, refer to the “Special Applications” section within the “Configuring the Wireless Cable/DSL Router” chapter of the User Guide.
If you are still experiencing any difficulties, proceed to the “Troubleshooting” section of this Guide.
The following graphic is a representation of your system topology after
the installation of the
Wireless Cable/DSL Router.